Figure 2.
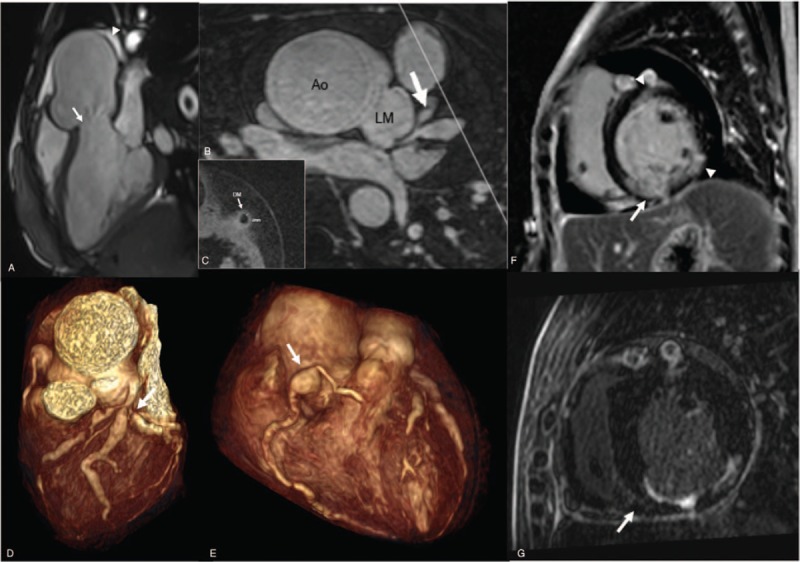
(A) Three-chamber cine image of cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) on admission shows aortic valve regurgitation (arrow) at the end-diastolic stage and pericardial effusion (arrowhead). (B) Multiplane reconstruction image of contrast-enhanced whole-heart coronary magnetic resonance angiography shows significant stenoses and dilutions involving the left anterior descending coronary artery and diagonal branch coronary artery (DM) (arrow). (C) Two-dimensional black blood coronary vessel wall image shows arterial wall thickening of the DM (2 mm). The white line in (B) defined the slice position where (C) was acquired. (D) VRT reconstruction image of CMR on admission shows severe left main coronary artery stenosis (arrow). (E) VRT reconstruction image of CMR on admission shows proximal right coronary artery (RCA) aneurysm (arrow). (F) Late gadolinum enhancement (LGE) image of CMR on admission shows subendocardial delayed enhancement of the mid anterior and mid inferolateral left ventricular wall (arrowhead), as well as transmural delayed enhancement of the basal inferior and mid inferior left ventricular wall (arrow). (G) LGE image of CMR 12 months later does not find new-onset delayed enhancement lesion. Ao = aorta, CMR = cardiac magnetic resonance, DM = diagonal branch coronary artery, LAD = left anterior descending coronary artery, LGE = late gadolinum enhancement, LM = left main coronary artery, MPR = multiplane reconstruction, RCA = right coronary artery, VRT = volume rendered reconstruction, WH-CMRA = whole-heart coronary magnetic resonance angiography.
