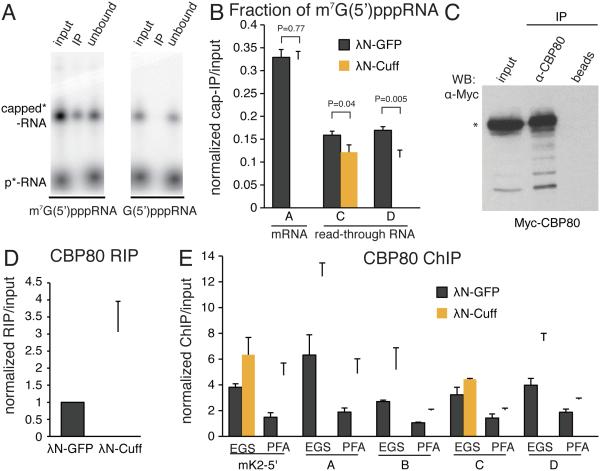
Fig. 6. Cuff stabilizes non-capped transcripts formed by cleavage at poly(A) sites.
(A) Anti-trimethylguanosine antibody specifically precipitates fully capped RNA. Radiolabeled RNAs with different groups at the 5’ end were precipitated with anti-trimethylguanosine antibody and bound (IP) and unbound fractions resolved on PAAG.
(B) Tethering of Cuff increases the fraction of non-capped read-through reporter transcripts. Capped RNA was immunoprecipitated from total ovarian RNA of flies that express the 4BoxB reporter shown on Fig 4A. Error bars show standard errors from six biological replicates. P values were calculated by t-test.
(C) Anti-CBP80 antibody specifically binds to Drosophila CBP80 protein. See also Figure S6.
(D) Tethering of Cuff increases association of CBP80 with reporter RNA. Ovarian lysates from flies expressing the 4BoxB reporter were used for RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) with anti-CBP80 antibody. Error bars are standard deviations from two biological replicates.
(E) Tethering of Cuff increases association of CBP80 with chromatin of the reporter locus. ChIP using paraformaldehyde (PFA) or ethylene glycol bis(succinimidyl succinate) (EGS) crosslinkers were used to determine association of CBP80 with several regions of the reporter shown in Fig. 4A. Error bars show standard errors from two technical replicates.