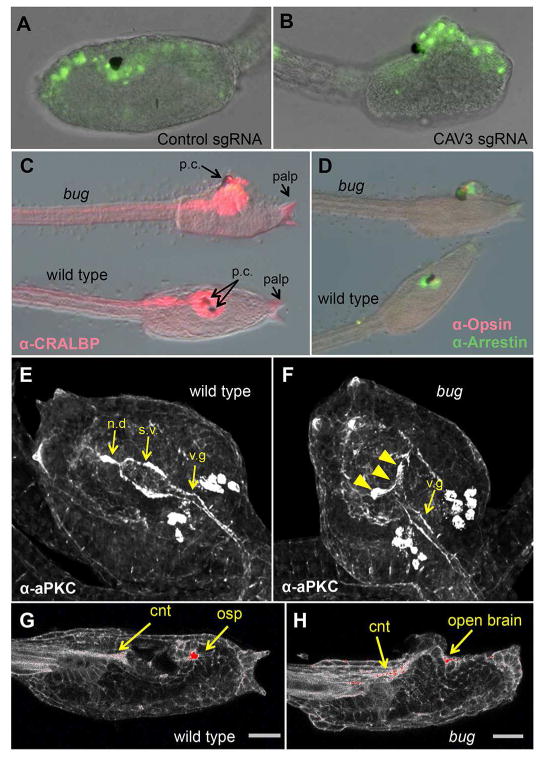
Figure 1.
CAV3 is required for Ciona intestinalis neural tube closure. A and B. Representative C. intestinalis embryos expressing a control guide RNA (sgRNA) (A), or guide RNAs targeting exons 3 and 49 of the C. intestinalis CAV3 gene (ciCAV3 sgRNA). See also Figure S1. (B). Green fluorescence from a pan-neural ETR1 promoter driving nuclear GFP construct marks neural tube cells. C and D. Bug mutants differentiate and polarize the anterior neural tube. Bugeye (bug) and wild type siblings stained for the neural markers CRALBP, Opsin and Arrestin, as indicated. E and F. Immunostaining for the cell polarity marker aPKC in wild type and bug mutants. s.v. = sensory vesicle, n.d.= neurohypophyseal duct, v.g.= visceral ganglion. The staining intensity is consistent between bug and wild type, although the sensory vesicle in bug embryos is open (arrowheads in F). Views are dorsal. G and H. Phalloidin staining of bug and wild type sibling larvae. The most intense staining is in red. cnt= caudal neural tube, osp=oral siphon primordium. Scale bar = 24 μm.