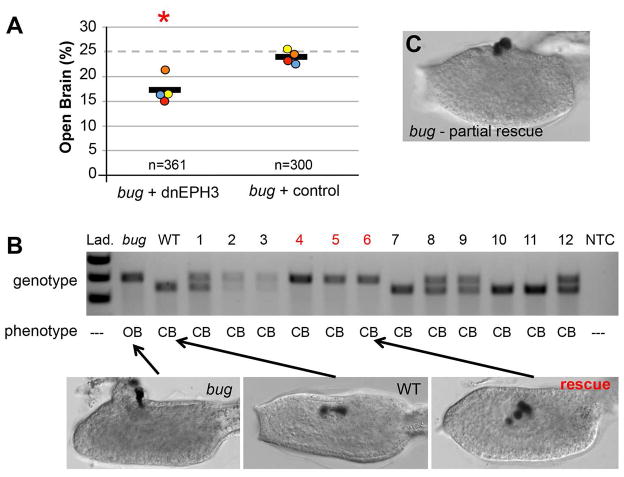
Figure 7.
Rescue of Ciona bugeye (bug) embryos with dominant negative EPH3 (dnEPH3). A. Embryos from heterozygous bug parents were electroporated with either dnEPH3 driven by the pan-neural promoter ETR1, or an empty ETR1 vector (control). The fraction of embryos with the bug phenotype (open brain) was determined for each group. Circles represent the percent of embryos showing the bug phenotype from four independent trials, and the black line is the average of the four trials (n is the combined number scored from the four trials). Red asterisks indicate significant P-value of 0.002 using a chi-squared test of deviation from the expected open brain frequency of 25%. B. Single tadpoles electroporated with dnEPH3 (lanes 1–12) and scored as having closed brains (CB) were genotyped with primers that distinguished the insertion-containing bug allele from the wild type allele. The bug and wild type (WT) lanes show the sizes the two alleles. Three of the twelve electroporated embryos (4–6, red) genotyped as homozygous for the bug allele despite having closed brains, and are considered as rescued. Representative images of wild type, bug, and rescued embryos are shown. See also Figure S2. C. Representative image of a partially rescued bug embryo.