Figure 3.
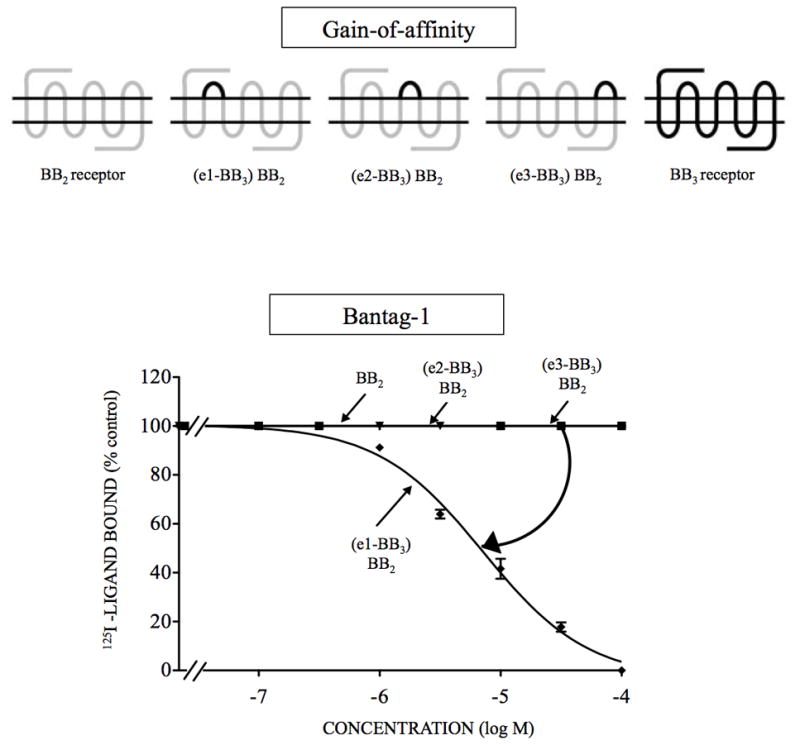
Affinities of the antagonist Bantag-1 for BB2 receptor gain-of-affinity BB2 chimeric receptors and BB3 receptor expressed in CHOP cells. The diagrams of the chimeric receptors formed are shown at the top. The chimeras BB2 receptors were formed by replacing each of the extracellular domains of BB2 receptor one at a time by the comparable BB3* receptor extracellular domain as described in Material and Methods. The different concentrations of Bantag-1 were incubated with 50 pM 125I- [D-Tyr6, β-Ala11, Phe13, Nle14]Bn- (6–14) for 60 minutes at 21°C in 300 μl of binding buffer with (e1-BB3) BB2 cells (0.6 x 106 cells/ml), (e2-BB3) BB2 cells (2 x 106 cells/ml), (eC3-BB3) BB2 cells (1.4 x 106 cells/ml) or BB2 receptor cells (7.0 x 106 cells/ml), and the saturable binding was determined as described under Materials and Methods. The results are expressed as the percentage of saturable binding without unlabeled peptide added (percentage control). The results are the mean and S.E.M. from at least three separate experiments and in each experiment the data points were determined in duplicated. The arrow indicates large change in affinity from the wild type BB2 receptor. Abbreviations: see Fig. 1 legend.
