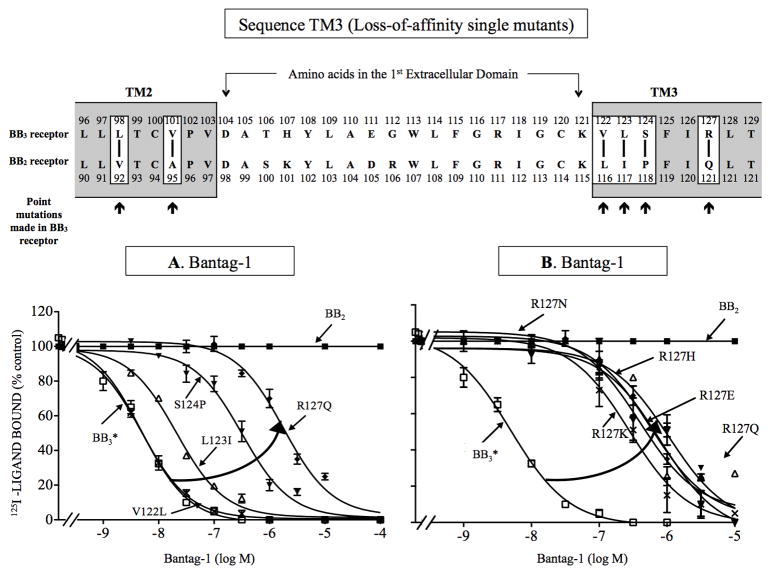
Figure 6.
Effect of single point mutations in the third transmembrane domain of BB3 receptor on affinity for Bantag-1 (loss-of-affinity BB3 receptor mutations). Top, alignment of amino acid sequences in the second and third transmembrane domain of BB3 and BB2 receptor. The boxes indicate divergent amino acids between these two receptors in these regions. Arrows indicate the position of the point mutations made in BB3 receptor by substituting into BB3* receptor the divergent amino acid from the comparable position in BB2 receptor. (A) Effect of four point mutants in BB3 receptor made to explore the importance of four amino acid differences in TM3 between BB3 and BB2 receptors for determining selectivity of Bantag-1. (B) Importance of the presence of a of charged amino acid in position 127 for determining selectivity of Bantag-1. The experimental conditions were the same as described in Fig. 1 legend. The results are expressed as the percentage of saturable binding without unlabeled peptide added (percentage control). The results are the mean and S.E.M. from at least three separate experiments and in each experiment the data points were determined in duplicated. Abbreviations: See in Fig. 1, 2 and 4 legends.