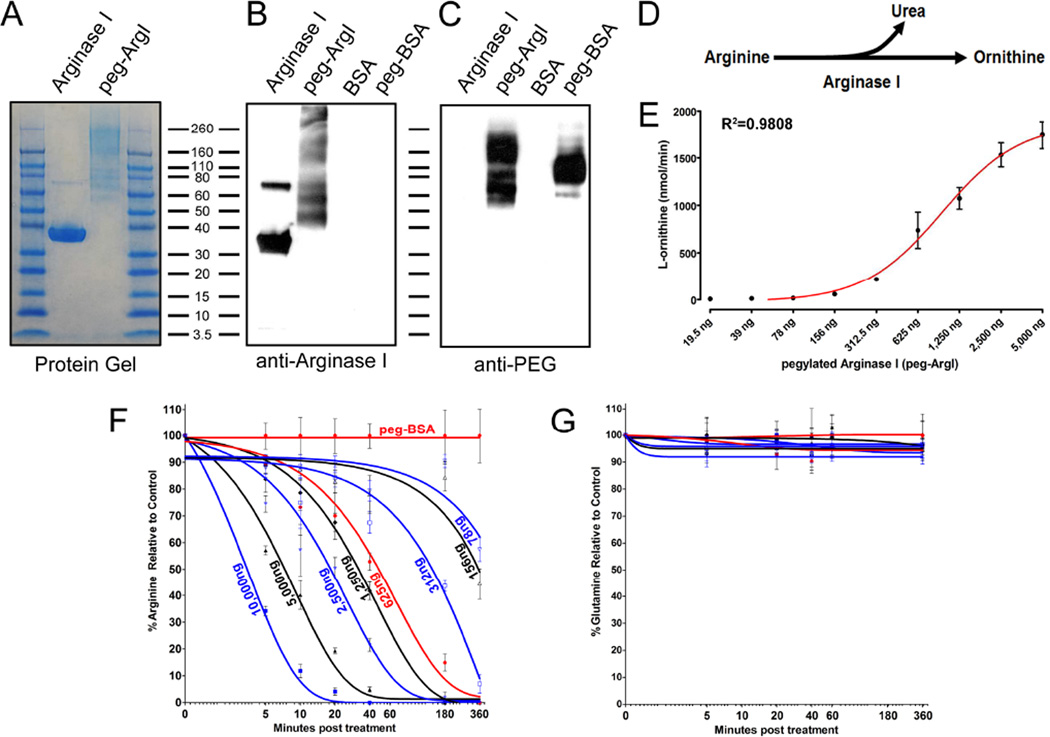
Figure 1.
Production and evaluation of an enzymatically active pegylated recombinant Arginase I for modulation of host arginine-associated metabolic pathways. Recombinant human ArgI was produced by expression in E. coli, column purified, and covalently conjugated to PEG-5000. (A) The purity of the purified recombinant ArgI, as well as the extent of pegylation were assessed by staining for total protein following SDS-PAGE (A). (B; C) The specificity of the expressed product and the presence of PEG was determined by western analysis for processed ArgI and control BSA using antibodies against either human ArgI (B) or PEG molecules (C). (D) ArgI catalyzes the hydrolysis of Arginine to Urea and Ornithine. (E) The enzymatic activity of 2-fold serially diluted concentrations of peg-ArgI was determined by measuring the conversion of arginine to the end-product L-ornithine. Each point represents the mean +/− the S.E.M. of samples analyzed in triplicate. (F; G) Dose-response and time-dependent effects of peg-ArgI treatment on the relative levels of either arginine (F) or glutamine (G). DMEM media was treated with serial 2-fold dilutions of peg-ArgI from 10µg/ml to 78ng/ml the levels of arginine or glutamine were determined in triplicate by HPLC at the time points indicated.