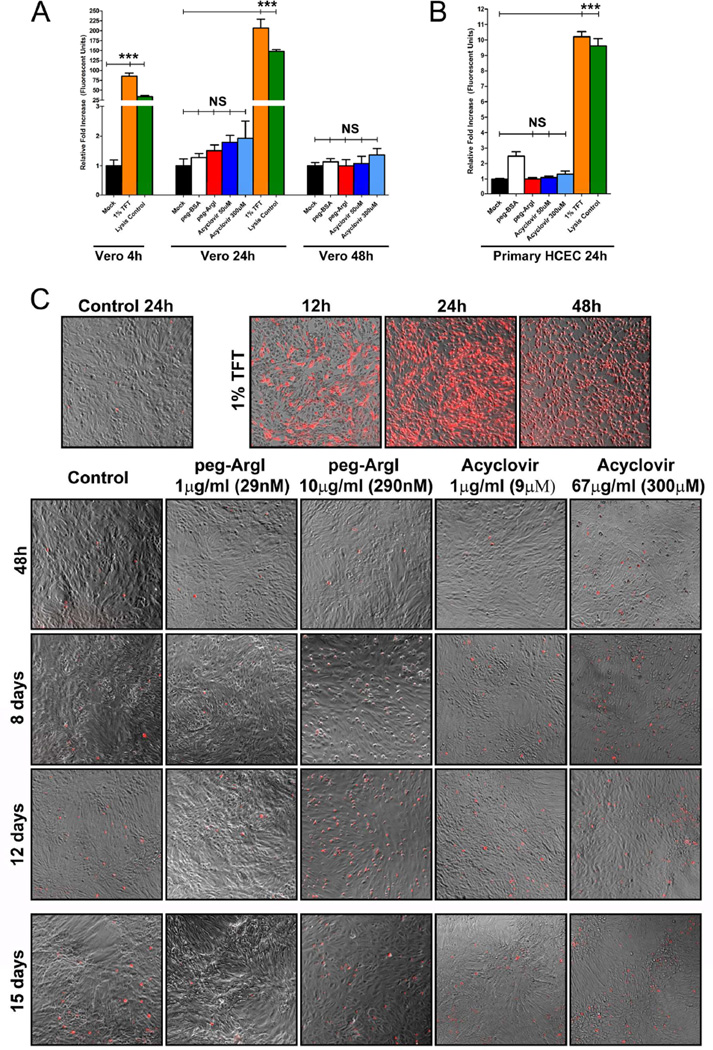
Figure 2.
peg-ArgI exhibits low cytotoxicity in both established and primary cells. The cytotoxicity of peg-ArgI (red) relative to the anti-herpetics, Acyclovir (shades of blue) or 1% Trifluorothymidine (TFT; orange), was determined in either CLSI standard (Sweirkosz, 2004) Vero cells (A) or primary human corneal epithelial cells (B) at 4, 24, or 48h post-treatment. Values from mock treated cells were set to 1 and cytotoxicity is expressed as a fold increase in toxicity relative to mock treatment (black). Detergent lysed cells (Lysis Control; green) were used as a positive control. Each bar represents the mean +/− the S.E.M. of five replicates. Experiments were repeated at least 3 times. (C) Comparison of long-term continuous treatment toxicity effects for peg-ArgI versus the anti-herpetics TFT or Acyclovir. Subconfluent Vero cells were continuously treated with individual drugs at the indicated concentrations for 12 days and relative toxicity was visualized at the days indicated by trypan blue exclusion assay and fluorescent microscopy. At day 12, the media was refreshed with new drug and final toxicity was visualized on day 15 post initial treatment.