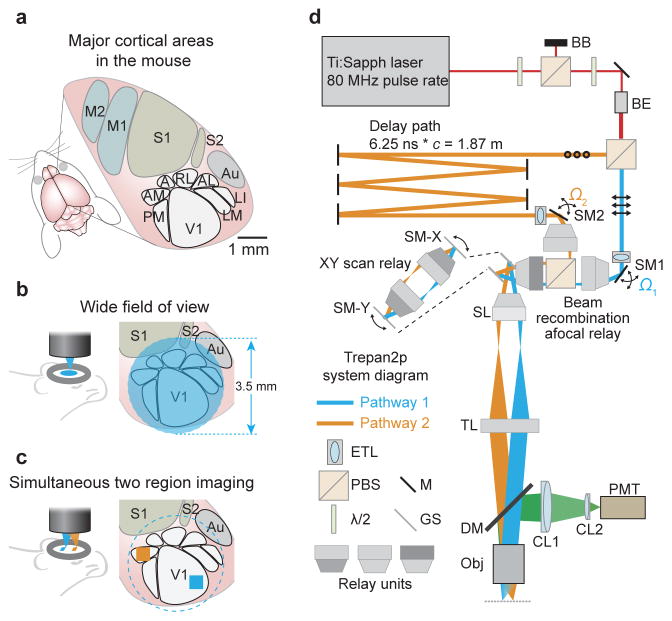
Figure 1. Treapn2p system layout.
(a) In the mouse, primary visual cortex (V1) is surrounded by higher visual areas (HVAs; PM = posteromedial; AM = anteromedial; A = anterior; RL = rostrolateral; AL = anterolateral; LM = lateromedial; LI = laterointermediate), which are distributed across several millimeters of cortex (M1,M2 = primary and secondary motor cortex; S1,S2 = primary and secondary somatosensory cortex; Au = auditory cortex). A wide field of view (FOV) is required to image neuronal activity in these distributed cortical areas simultaneously. (b) The 3.5 mm FOV can encompass V1 and HVAs. (c) The individual imaging regions can be independently positioned and repositioned anywhere within the full FOV by the steering mirrors (SM1, SM2 in d) for XY position, and the tunable lenses (ETL in d) for independent Z positioning. (d) Two imaging beams are temporally multiplexed and independently positioned in XY and Z prior to the scan mirrors (SM-X, SM-Y). First, overall power is attenuated using a half-wave plate (λ/2), a polarizing beam splitting cube (PBS) and a beam block (BB). After a second λ/2 (used to determine the power ratio sent to the two pathways) and a beam expander (BE), a second PBS divides the beam into two pathways. Pathway 1 (in blue, p-polarization, indicated by the arrows) passes directly to a motorized steering mirror (SM1) for positioning in XY. Pathway 2 (in orange, s-polarization, indicated by the circles) passes to a delay arm where it travels 1.87 meters further than pathway 1 using mirrors (M), thus delaying it by 6.25 ns before being directed to SM2. Directly prior to SM1 and SM2 are electrically tunable lenses (ETL) that can adjust the Z position (focal plane) of the pathways independently. The two pathways are recombined (beam recombination relay), and sent to X and Y galvanometer scanners (GS) that are connected by an afocal relay (expanded view inset). A scan lens (SL) and tube lens (TL) focuses the two multiplexed beams onto the back aperture of the objective (Obj). Fluorescence is directed to a photomultiplier tube (PMT) via an infrared-passing dichroic mirror (DM) and two collection lenses (CL1, CL2).