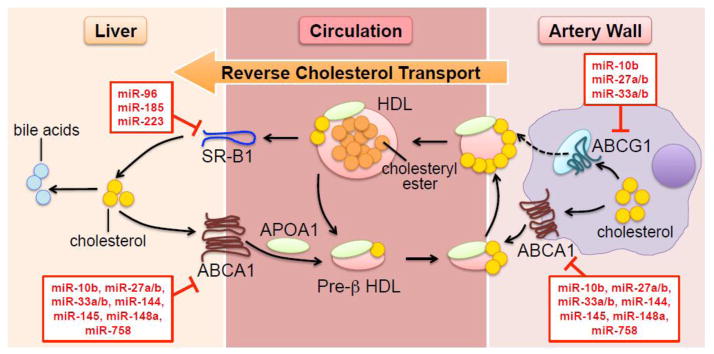
Fig. 1. Mobilization of cholesterol via HDL particles.
The lipidation of lipid-poor APOA1 in the hepatocyte (and in minor proportion in the enterocyte and adipocyte) generates pre-β HDL, which is further lipidated in the peripheral vasculature via ABCA1 and possibly ABCG1. Unesterified cholesterol in the nascent particle is esterified by LCAT. HDL exchanges lipids and apolipoproteins with APOB-containing lipoproteins (not shown in the figure). Clearance of HDL-bound cholesteryl esters is facilitated by SR-B1 in the liver. Excess hepatic cholesterol is eventually metabolized to bile acids and excreted through bile. miRNAs known to target transcripts involved in HDL biogenesis and the reverse cholesterol transport pathway are annotated in red boxes.