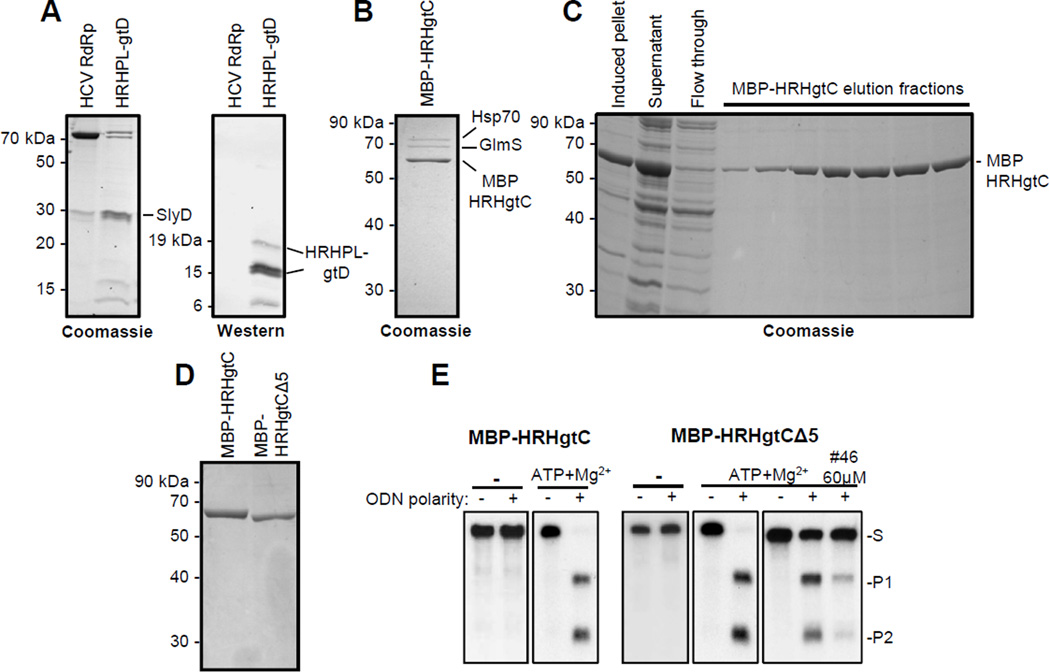
Figure 2. Purification of dual-tagged recombinant HBV RNaseH.
A. Enriched extracts of HRHPLgtD following nickel-affinity chromatography were analyzed by Coomassie-blue staining an SDS-PAGE gel and by western blot employing monoclonal antibody 9F9 which recognizes an epitope at the C-terminus of the HBV polymerase. This panel is modified from (Tavis et al., 2013a) under the Creative Commons Attribution license. B. Coomassie staining of an SDS-PAGE analysis of the final nickel-affinity chromatography elution fraction for MBP-HRHgtC purification done in the absence of ATP and Mg2+. C. Purification of HBV MBP-HRHgtC in the presence of ATP and Mg2+. D. Comparison of the final purification products for MBP-HRHgtC and MBP-HRHgtCΔ5 isolated in the presence of ATP and Mg2+ by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. E. RNaseH activity in the ODN-directed RNaseH assay for MBP-HRHgtC (2.4 µg/reaction) and MPB-HRHgtCΔ5 (1.3 µg/reaction) purified in the absence (−) or presence of ATP and Mg2+. Inhibition of MBP-HRHgtCΔ5 (0.26 µg/reaction) purified in the presence of ATP and Mg2+ is shown at right; #46 is the HBV RNaseH inhibitor β-thujaplicinol. S, substrate; P1, product 1; P2, product 2.