Fig. 6.
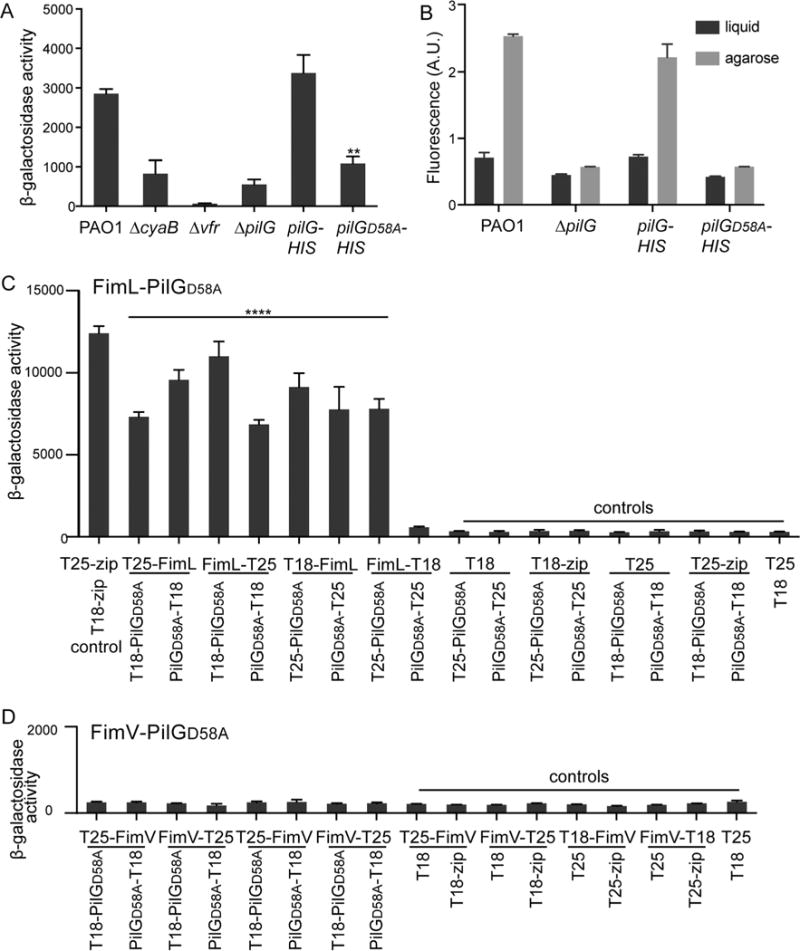
PilG phosphorylation is required for cAMP production and contact-dependent gene activation but not for its association with FimL or its FimV-dependent polar localization.
A. β-galactosidase activity (A420 min−1 mL−1 of cells measured at OD600) of the indicated strains expressing the Placp1-lacZ reporter gene. cAMP levels directly correlate with β-galactosidase activity from the lacp1 promoter. Shown are mean ± SEM (N = 2 biological replicates, with three technical replicates each). ** P ≤ 0.005 PAO1∷PilGD58A-HIS compared to PAO1∷PilG-HIS. The difference between PAO1 compared to PAO1∷PilG-HIS was not significant.
B. Contact-dependent cAMP/Vfr-dependent gene transcription was quantified as described for Fig. 4. The individual fluorescent ratios of ~ 100 cells were determined. Shown is the mean ± SEM of 3–4 biological replicates.
C and D. β-galactosidase assays were performed on liquid-grown BTH101 E. coli transformed with the indicated plasmid pairs. Results are expressed as Miller units of β-galactosidase activity (A420 min−1 mL−1 of cells measured at OD600). Shown are Mean ± SEM (N = 3 biological replicates with three technical replicates each). C. **** P ≤ 0.0001 for all combinations of FimL/PilGD58A pairs relative to all negative controls except FimL-T18/PilGD58A-T25, D. ns for all combinations of FimV/PilGD58A relative to all controls.
