Fig. 8.
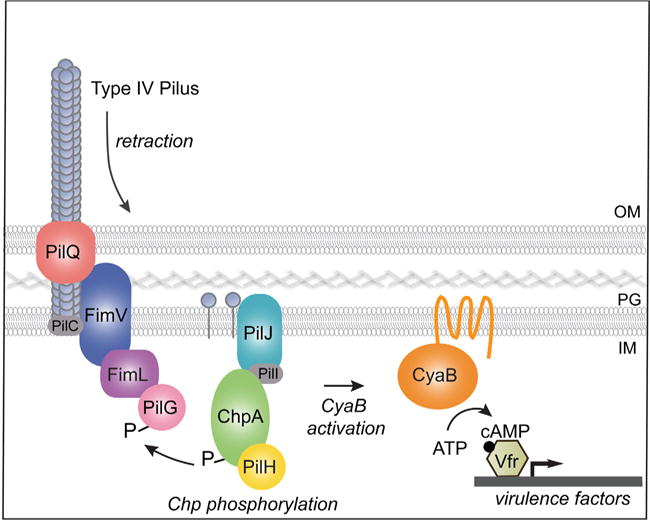
Model for surface-activated regulation of cAMP/Vfr-dependent virulence factors. On surface binding, TFP retracts. Depolymerized or conformationally altered pilin monomer binds to PilJ in the periplasmic and/or inner membrane space, which leads to ChpA histidine kinase autophosphorylation. A phosphoryl group is subsequently transferred to the response regulator PilG, which leads to stimulation of the membrane bound adenylate cyclase CyaB, cAMP production and activation of cAMP/Vfr-dependent virulence circuits. FimV is required for polar localization of FimL and PilG. Our studies show that FimV, FimL and phosphorylation-competent PilG are required to stimulate cAMP production and surface-mediated activation of a cAMP/Vfr-dependent promoter. In addition, we show that FimL binds to FimV and to PilG, although whether they form a trimolecular complex is unknown. We speculate that localization of PilG to the pole through its binding to FimL and FimV increases its local concentration and facilitates its phosphorylation by ChpA.
