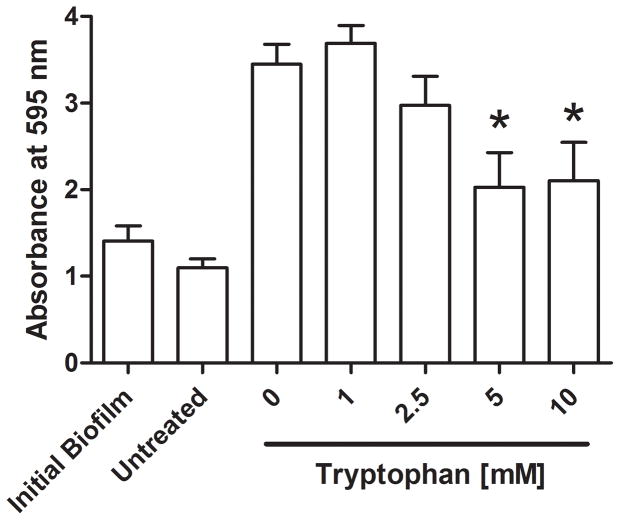
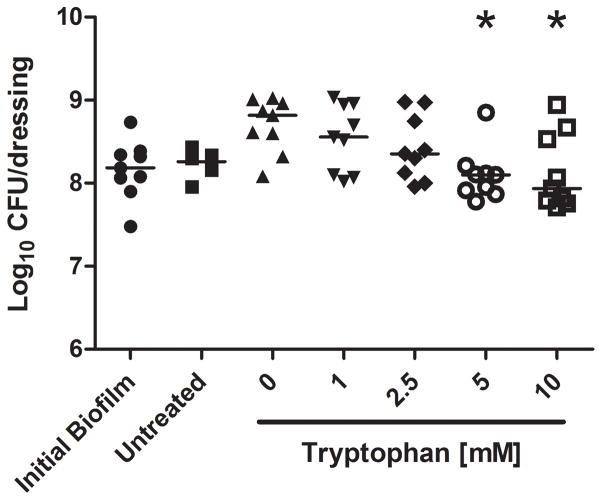
Figure 5. Tryptophan treatment of established P. aeruginosa biofilms.
P. aeruginosa biofilms were grown for 48 hours at 30°C on the biological wound dressing prior to treatment with tryptophan (0 – 10 mM). The treatment lasted for an additional 24 hours at 30°C. A) Crystal violet staining revealed that tryptophan significantly inhibited additional biofilm growth (*, p<0.05) and that concentrations above 5mM were not significantly higher than the initial biofilm. B) Quantification of bacterial cells attached to the dressing showed that tryptophan significantly reduced additional bacterial colonization compared to the fresh media alone (*, p<0.05), concentrations of tryptophan above 1mM were not significantly different than the initial bacterial load on the dressing.