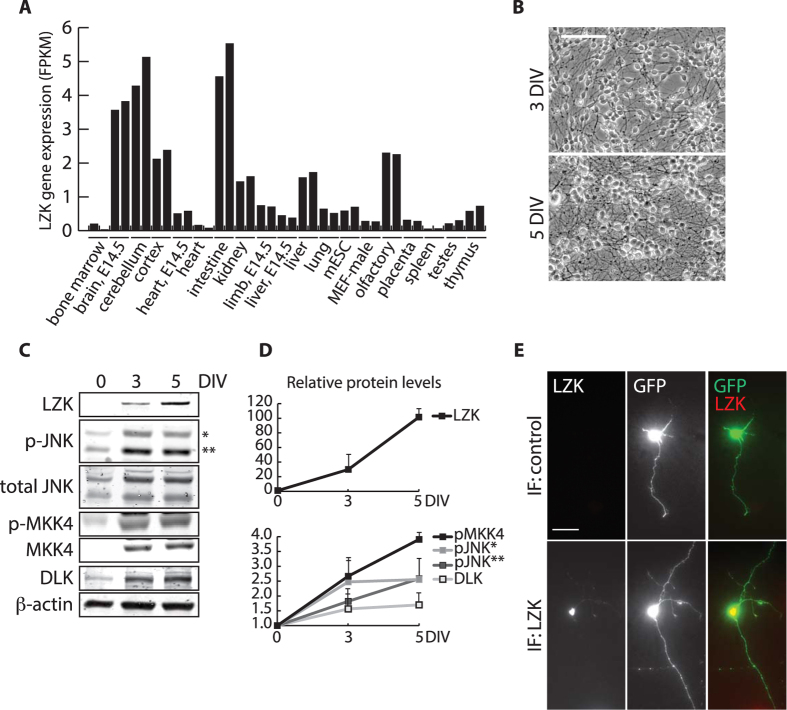
Figure 3. Neuronal maturation-dependent upregulation of LZK-MKK4-JNK in cerebellar granule neurons.
(A) Graph compares gene expression of LZK in nineteen tissues from adult and embryonic (E14.5) mice based on published RNA-Seq dataset30. Each tissue sample was run in duplicates. LZK expression level is presented as fragments per kilobase of exon per million fragments mapped (FPKM). (B) Bright field images show axon growth of primary cerebellar granule neurons (CGNs) isolated from postnatal (P7) mice cultured for 3 and 5 days in vitro (DIV). Scale bar = 50 μm. (C) Total cell lysates from CGNs cultured for 0 (freshly dissociated cells before plating), 3, and 5 DIV were immunoblotted for the indicated endogenous proteins. *JNK 54 kDa isoform; **JNK 46 kDa isoform. (D) Based on (C) graphs show immunoblot signal-based quantification of endogenous LZK, p-JNK1/2, and p-MKK4 protein levels that were first normalized to β-actin in the corresponding samples, followed by subsequent normalization of this ratio on 3 and 5 DIV to that of 0 DIV (presented as baseline of 1 on graphs). *JNK 54 kDa isoform; **JNK 46 kDa isoform. (E) CGNs transfected with pBI empty vector expressing GFP for visualization of cell morphology were cultured for 3 DIV and immunostained for endogenous LZK (top panel), or with secondary antibody only as negative control (bottom panel). Scale bar = 50 μm.