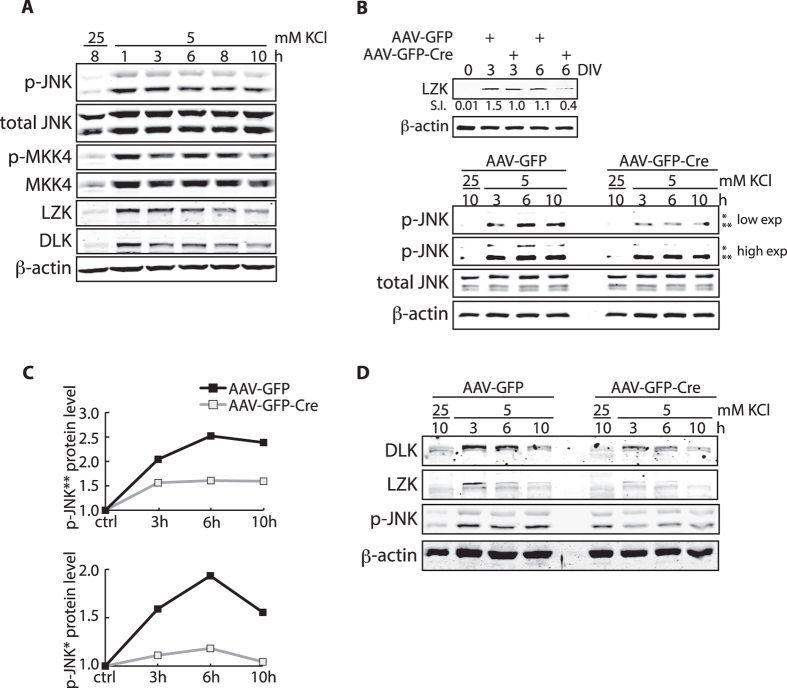
Figure 7. Silencing of neuronal activity by potassium withdrawal leads to LZK-dependent activation of JNKs in cerebellar granule neurons.
(A) CGNs from wild-type mice were maintained in media containing 25 mM KCl for five days. Potassium withdrawal was performed by switching to media containing 5 mM KCl without serum as previously described39 on day 6. CGNs were collected at the indicated times following potassium withdrawal and total cell lysates were immunoblotted for the indicated endogenous proteins. (B) LZKT/T CGNs were infected with AAV-GFP or AAV-GFP-Cre 40 hours after plating. Top panel, total cell lysates collected on 0, 3, 6 DIV were immunoblotted for endogenous LZK to assay LZK depletion in the total cell population. Immunoblot-based quantification of signal intensity (S.I.) of endogenous LZK protein levels normalized to that of β-actin is shown. Bottom panel, AAV-GFP or AAV-GFP-Cre infected LZKT/T CGNs were subjected to potassium withdrawal on 6 DIV. Total cell lysates collected at the indicated times following treatment were immunoblotted for the indicated endogenous proteins. Two different exposures (low and high) for p-JNK2 and p-JNK1 are shown for better comparison. *JNK 54 kDa isoform; **JNK 46 kDa isoform. (C) Graphs quantify endogenous p-JNK protein levels from the bottom panel in (B). Immunoblot-based quantification of JNK protein expression was first normalized to β-actin in the corresponding sample, and shown as a value relative to the control (presented as baseline of 1). (D) LZKT/T CGNs were infected with control AAV-GFP or AAV-GFP-Cre 40 h after plating. AAV-infected LZKT/T CGNs were subjected to potassium withdrawal on 6 DIV. Total cell lysates collected at the indicated times following treatment were immunoblotted for the indicated endogenous proteins.