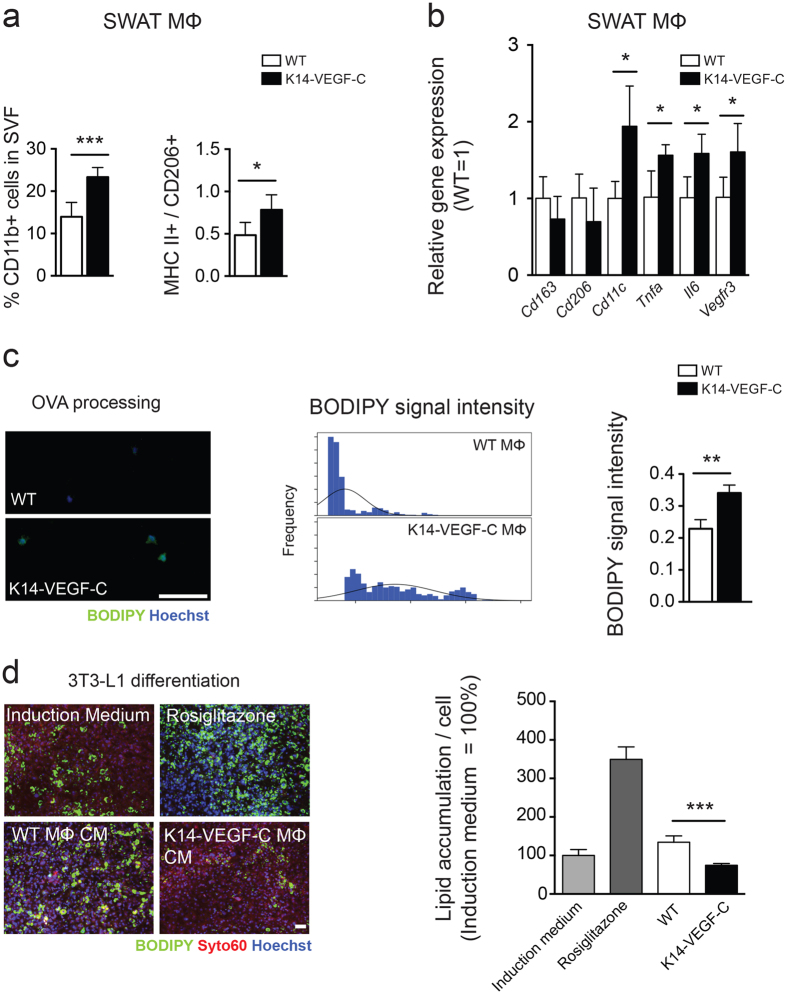
Figure 5. SWAT macrophages of K14-VEGF-C mice show enhanced pro-inflammatory characteristics before the onset of increased adiposity.
(a) Data from 22-week-old mice, (b–d) data from 14-week-old mice; prior to the onset of weight gain. (a) Increased percentage of CD11b+ cells in SWAT stromal vascular fraction, with a significant elevation of M1/M2 macrophage marker ratios in K14-VEGF-C mice. (b) Gene expression analysis of M2 (CD163, CD206) and M1 (CD11c, TNF-α, IL6) markers showed a boosted M1 phenotype in isolated K14-VEGF-C SWAT macrophages from 14-week-old mice (n = 3–4). (c) Increased BODIPY fluorescence signal revealed by enhanced OVA processing of K14-VEGF-C SWAT macrophages; histograms show the distribution of BODIPY signal intensity and the corresponding quantification per mouse (n = 3 mice per group, scale bar = 100 μm). (d) Conditioned media from SWAT macrophages of K14-VEGF-C, but not WT mice, significantly reduced the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells in vitro (n = 4 mice per group, scale bar = 200 μm). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-test. Data are mean ± SD.