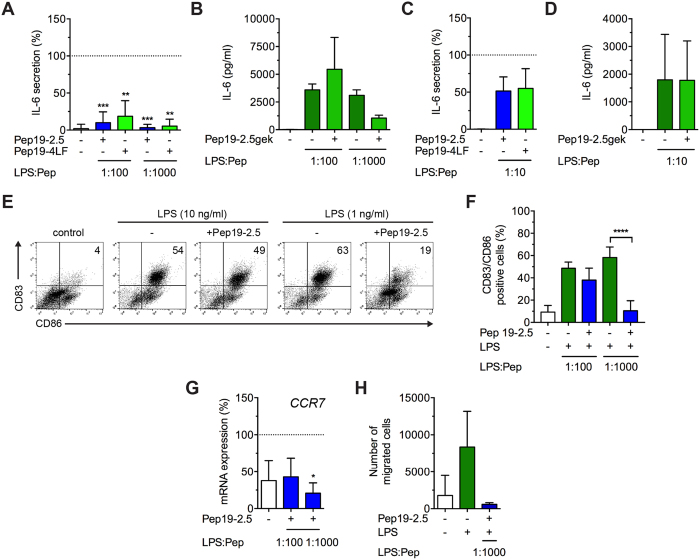
Figure 4. SALPs inhibit LPS-induced cytokine secretion, maturation and CCR7-dependent migration of dendritic cells.
(A,B) MoDCs were stimulated with 1 or 10 ng/ml LPS (MoDCs) and (C,D) MoLCs with 100 ng/ml LPS together with 20 ng/ml TNF and 10 ng/ml IL-1β in the presence or absence of the peptides (1 μg/ml) for 24 h, supernatants were collected and IL-6 production was quantified by ELISA. Data are mean + SD (n = 3-8). *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, one-sample t test. (E) MoDCs were stimulated with 1 or 10 ng/ml LPS in the presence or absence of Pep19-2.5 (1 μg/ml) for 24 h and surface expression of CD83 and CD86 was analysed by two-colour flow cytometry. Dot Plots are representative for 3 independent experiments and percentage of stained cells is indicated. (F) Bar chart summarizes means of double-positive cells. Mean + SD (n = 3). ***p ≤ 0.001, one-sample t test. (G) MoDCs were stimulated with 10 ng/ml LPS in the presence or absence of Pep19-2.5 for 24 h and gene expression of CCR7 was analysed by qPCR. mRNA expression values were normalised to YWHAZ. Data are mean + SD (n = 3). *p ≤ 0.05, one-sample t test. (A,C,G) Data were normalised to LPS-treated cells in the absence of the peptides (100%). (H) MoDCs were stimulated with 1 ng/ml LPS in the presence or absence of Pep19-2.5 for 48 h. Cell migration was evaluated after 2.5 h towards the ligand CCL21 (100 ng/ml) by flow cytometry. Data are mean + SD (n = 4).