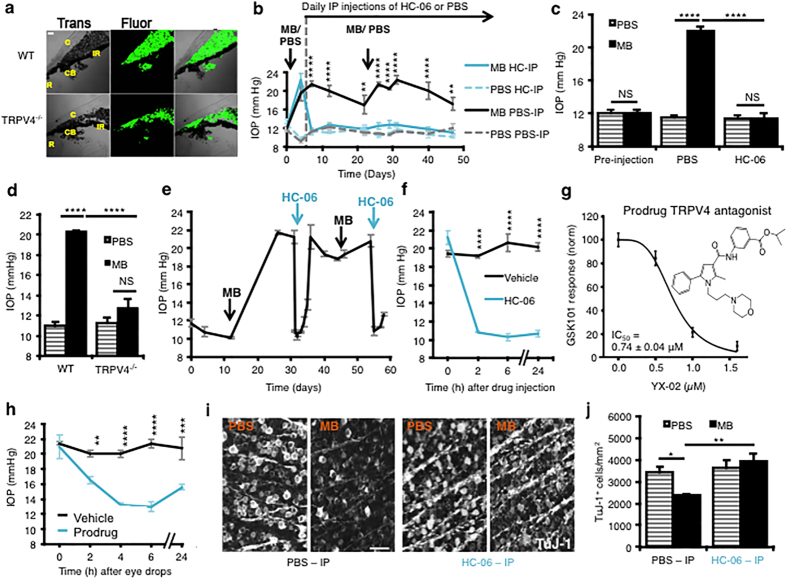
Figure 6. TRPV4 inhibition lowers IOP elevation and protects RGCs in a mouse glaucoma model.
(a) Injected microbeads clog the anterior chamber in WT and Trpv4−/− eyes 7 days post-injection; bright-field transmitted image (left panel) and fluorescent image (middle panel). Abbreviations: C, cornea; R, retina, CB, ciliary body, IR, iris. Scale bar = 50 μm. (b) Intracameral injection of MBs (black trace) but not vehicle (PBS; dashed grey trace) elevates IOP. Subsequent daily IP delivery of HC-06 (solid blue trace) lowered IOP to baseline, whereas vehicle injection had no effect (dashed light blue trace). MBs and PBS were re-injected into the anterior chamber to maintain IOP elevation (second arrow). (c) Cumulative data for the effects of MB/PBS injection in the presence/absence of the TRPV4 antagonist 7 weeks post-injection (N = 4 experiments; N = 10–15 animals per experimental group). (d) MB injection into WT, but not Trpv4−/−, eyes (N = 4 mice) elevates IOP above levels in PBS injected eyes. (e) Intraocular injection of HC-06 (100 μM) resulted in long-lasting lowering of IOP in MB-injected eyes. (f) Intraocular injections at a shorter time scale. (g) Chemical structure of the putative prodrug analog YX-02: isopropyl 3-(2-methyl-1-(3-morpholinopropyl)-5-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxamido)benzoate (IUPAC). YX-02 dose-dependently suppresses GSK101 (25 nM)-induced Ca2+ signals in hTM cells. (h) A single topical application of the prodrug was sufficient to decrease IOP for ~24 hours in MB-injected eyes (n = 4 animals) whereas the vehicle (PBS) had no effect. (i,j) Retinal wholemounts isolated after 2 months of IOP elevation. The density of Tuj-1+ cells in the RGCL was significantly reduced, whereas daily IP HC-06 injection protected the cells from elevated IOP (N = 3 experiments; n = 10–15 animals per experimental group). Scale bar = 50 μm.