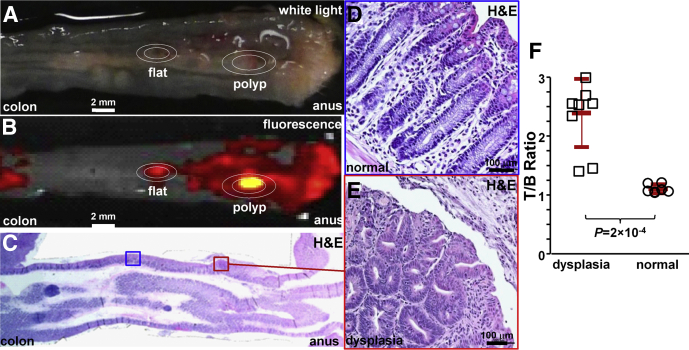
Figure 8.
Ex vivo validation of peptide binding to colonic dysplasia. (A) Representative white-light image of excised distal 2 cm of mouse colonic mucosa accessed by endoscopy after RTS*-Cy5.5 was administered topically in vivo. (B) Near-infrared image shows regions of increased fluorescence intensity. (C) Histology (H&E) sectioned parallel to mucosal surface was evaluated for the presence of dysplasia by an expert gastrointestinal pathologist (S.R.O.). Expanded views of (D) normal and (E) dysplasia (original magnification: 20×). (F) From 3 mice, the mean (±SD) T/B ratio was significantly higher for 9 regions of dysplasia compared with 7 normal (2.4 ± 0.6 vs 1.1 ± 0.1, respectively; P = 2 × 10-4 by unpaired t test).