Figure 1.
Structural Modeling and ND-PAGE Mobility Shift Assay of CNGC12 CaMBD Peptides.
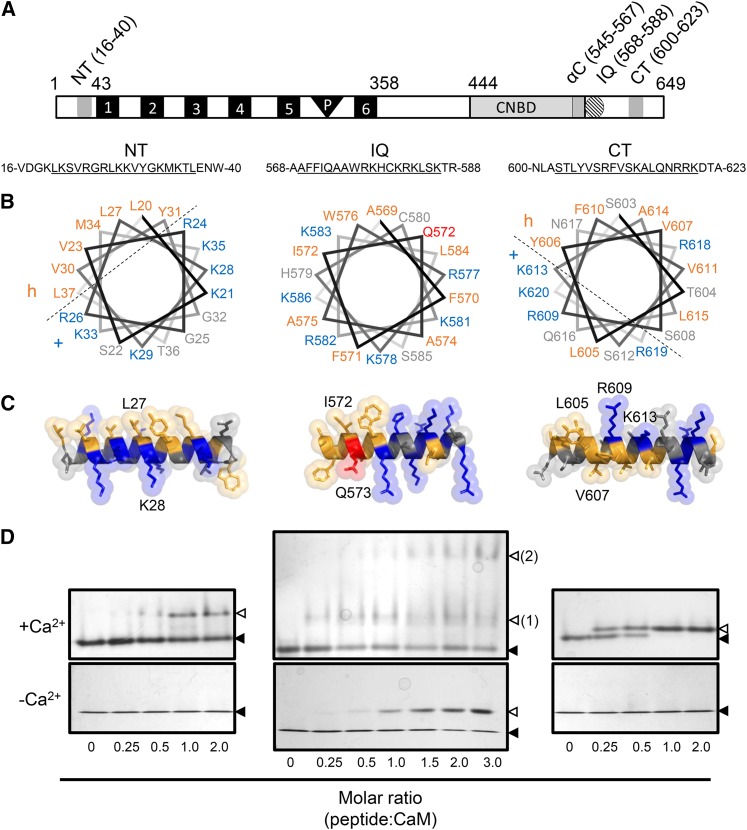
(A) Location of the CaMBDs of CNGC12 (see delineation of NT and CT sites in Supplemental Figure 1). Numbers indicate amino acid position. 1 to 6, Transmembrane helices; P, pore region.
(B) Helical wheel projections of motifs for the NT, IQ, and CT peptides (underlined sequences). Dashed lines separate proposed hydrophobic (h) and basic (+) faces of the NT and CT wheels.
(C) 3D model of full-length CaMBD peptides. Specific residues used for mutant analysis of each motif in this work are indicated in each model. In both (B) and (C), hydrophobic and basic residues are colored orange and blue, respectively, while the Q573 residue of the IQ motif is also colored (red) due to its suspected involvement in CaM binding.
(D) ND-PAGE mobility shift assays in the presence of 0.1 mM CaCl2 (top panels) or 2 mM EGTA (bottom panels). Closed triangles indicate the migration size of CaM alone, while open triangles indicate the migration size of CaM-peptide complex. Two distinct IQ-CaM complexes consistently migrated separately in Ca2+/CaM assays with IQ peptide (top panel, numbered 2); such a pattern was never observed with NT or CT peptides or in any apoCaM assays.