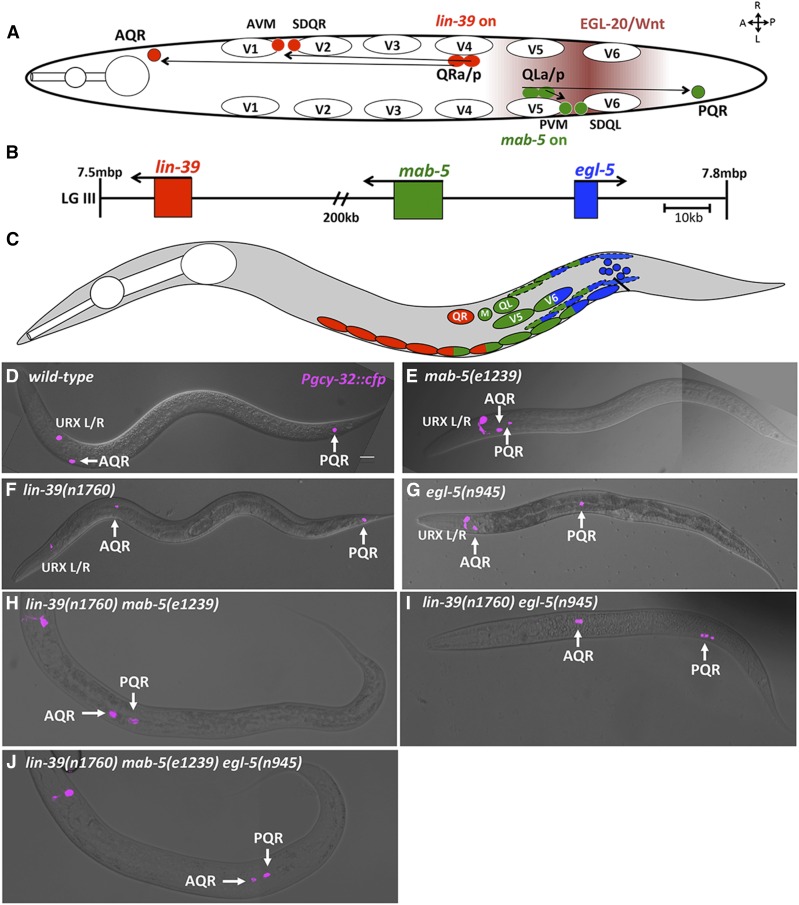
Figure 1.
C. elegans Hox genes lin-39, mab-5, and egl-5 affect Q descendant migrations. (A) Diagram of a dorsal view of wild-type Q descendant migration. EGL-20/Wnt (maroon shading) induces MAB-5 in QL and descendants, which directs posterior migration. QR and descendants do not respond to EGL-20/Wnt, and express lin-39, driving anterior migration. (B) Position on LGIII (7.5–7.8 Mbp) of the three C. elegans Hox genes that effect postembryonic development. (C) representation of cells that express lin-39 (red) , mab-5 (green), and egl-5 (blue) during the L1 larval stage. Dashed ovals represent BWMs, solid ovals the P cells, and blue circular cells near the anus represent the rectal epithelium where egl-5 is expressed. (D–J) Positions of Q descendants AQR and PQR in L4/young adult animals. lqIs58[Pgcy-32::cfp] micrographs were merged with DIC micrographs in wild-type and mutants. In all micrographs unless otherwise noted, dorsal is up, anterior is left. Bar, 10 μm.