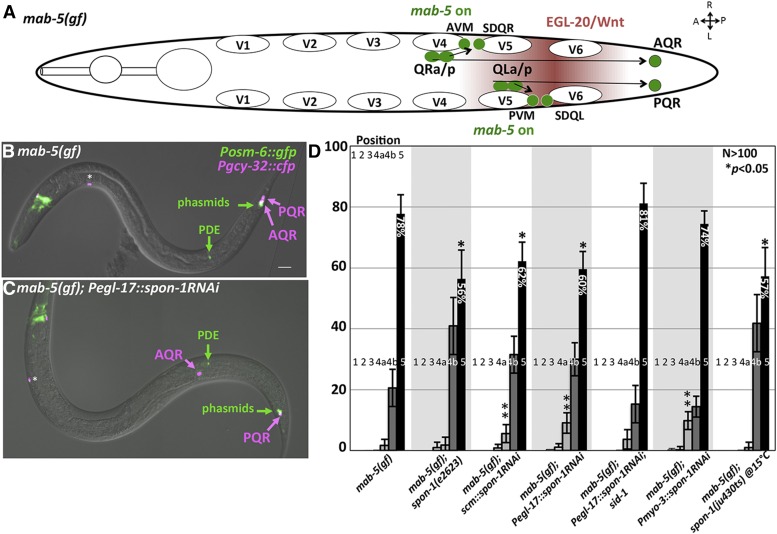
Figure 12.
Suppression of mab-5(gof) by spon-1. (A) Diagram of Q descendant migration in mab-5(e1751) gain-of-function mutants as described in Figure 1A. mab-5 is ectopically expressed in QR lineages, causing its descendants including AQR to migrate posteriorly. (B and C) Merged DIC and fluorescent micrographs of mab-5(gof) animals. Posm-6::gfp marks the PDE neuron, which serves as a landmark for Q birth position. The asterisk indicates an unidentified cell body present in mab-5(gof), but not wild type, that expresses Pgcy-32::cfp. (D) Quantification of AQR position in mab-5(e1751)gof mutants alone and in double mutant combination (see Figure 2). Asterisks indicate a significant (P < 0.05, Fisher’s exact test) reduction in the percentage of AQR residing in position 5 compared to mab-5(gof). Double asterisk refers to genotypes with a significant increase in anterior migration (position 4a or more anterior) compared to mab-5(gof). The locations 4a and 4b refer to location within position 4, with 4a anterior to PDE, and 4b posterior to PDE. Error bars represent 2× standard error of the proportion. Pscm and Pegl-17 spon-1 RNAi genotypes represent a combination of two independently derived transgenic lines with similar effects, and the Pmyo-3 line represents combined results of three independent transgenic lines with similar effects.