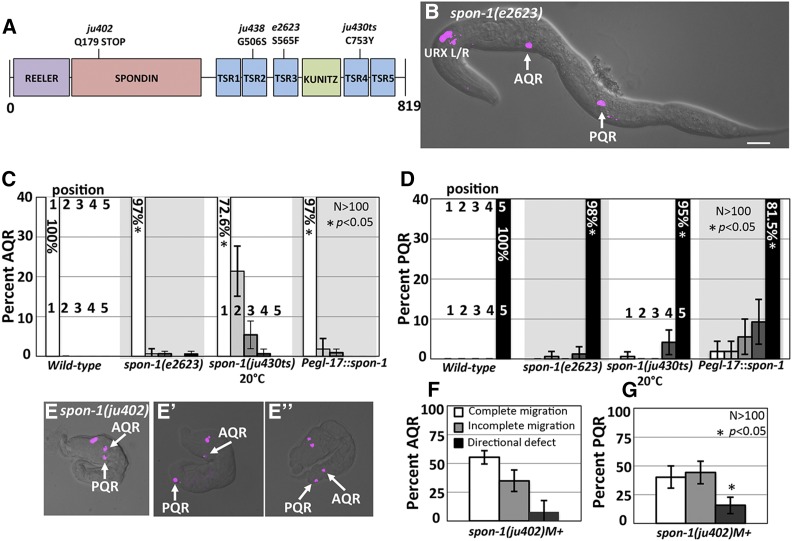
Figure 5.
AQR and PQR migration defects in spon-1 mutants. (A) Diagram of the predicted 819-residue SPON-1 molecule with Reeler, Spondin, Thrombospondin (TSR), and Kunitz serine protease inhibitor (KUNITZ) domains shown. The positions of mutations are indicated. (B) A spon-1(e2623) young adult animal with defects in AQR and PQR migration (merged cfp and DIC micrographs). Bar, 20 μm. (C and D) AQR and PQR migration defects in spon-1 as described in Figure 2. Error bars represent 2× standard error of the proportion. (E–E′′) spon-1(ju402)M+ arrested L1 animals with Pgcy-32::cfp. (E) PQR reversal in migration direction. (E′) Complete AQR and PQR migration. (E′′) AQR directional defect. (F and G) Percent of AQR (F), and PQR (G) that show defects in spon-1(ju402)M+-arrested L1 animals.