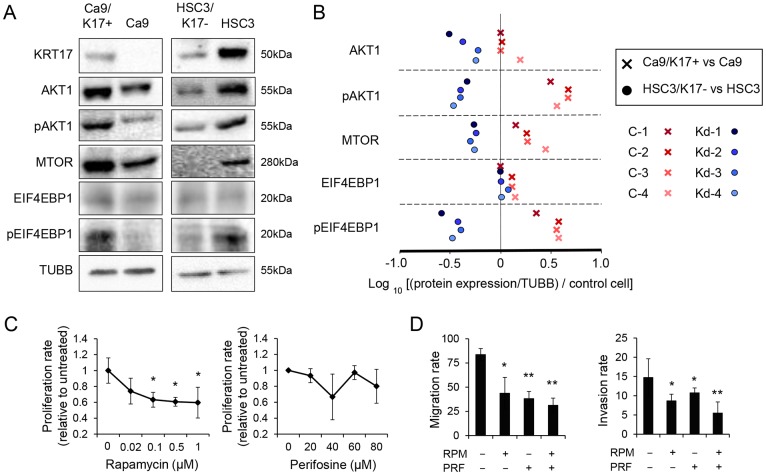
Fig 4. KRT17 stimulated the Akt and mTOR pathway.
(A) Representative images of western blot analysis of Ca9/K17+ (C-4), Ca9, HSC3/K17- (Kd-4), and HSC3 for detecting KRT17, AKT1, phosphorylated AKT1 (pAKT1), MTOR, EIF4EBP1, phosphorylated EIF4EBP1 (pEIF4EBP1), and beta1-tubulin (TUBB). Quantitative results measured by densitometric analysis of all the clones (C-1 to C-4 and Kd-1 to Kd-4) are shown in (B). Representative images of two assays. (B) Expression of AKT1, pAKT1, MTOR, EIF4EBP1 and pEIF4EBP1 in Ca9/K17+ (C-1, C-2, C-3, and C-4) and HSC3/K17- (Kd-1, Kd-2, Kd-3, and Kd-4) compared with Ca9 and HSC3, respectively, as revealed by densitometric analysis of the western blots. Expression level of protein X in a clone was normalized against TUBB and then against the control cells using the formula (Value of protein X in the clone / Value of TUBB in the clone) / (Value of protein X in the control cells / Value of TUBB in the control cells). The normalized expression levels were plotted on a log scale. Representative results of two independent assays that showed similar results. (C) Effect of mTOR-inhibitor rapamycin (RPM) and Akt-inhibitor perifosine (PRF) on proliferation of Ca9/K17+ (C-4) cells. Ca9/K17+ cells were treated with different concentrations of either RPM or PRF for 72 h and cell densities were measured. Representative graphs of three assays that showed similar results, each performed with n = 3 technical replicates. *P < 0.05 compared with the untreated control. Data represent mean ± SEM. (D) Transwell migration assay of Ca9/K17+ (C-4) treated with RPM and/or PRF (left panel). Transwell invasion assay of Ca9/K17+ (C-4) treated with RPM and/or PRF (right panel). Representative graphs of three assays that showed similar results, each performed with n = 3 technical replicates. **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05 compared with the untreated control. Data represent mean ± SEM.