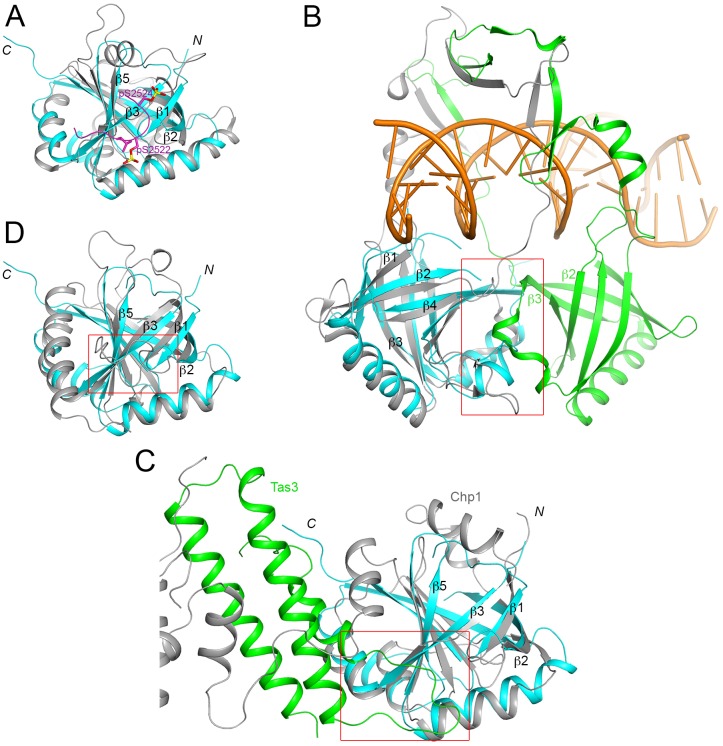
Fig 3. Structural homologs of the FPA SPOC domain.
(A). Overlay of the structures of the FPA SPOC domain (cyan) and the SHARP SPOC domain (gray). The bound position of a doubly-phosphorylated peptide from SMRT is shown in magenta. (B). Overlay of the structures of the FPA SPOC domain (cyan) and the Ku70 β-barrel domain (gray). Ku80 contains a homologous domain (green), which forms a hetero-dimer with that in Ku70. The two domains, and inserted segments on them, mediate the binding of dsDNA (orange). The red rectangle highlights the region of contact between the two β-barrel domains. (C). Overlay of the structures of the FPA SPOC domain (cyan) and the homologous domain in Chp1 (gray). The binding partner of Chp1, Tas3, is shown in green. The red rectangle indicates the region equivalent to the binding site of the SMART phosphopeptide in SHARP SPOC domain, where a loop of Tas3 is also located. (D). Overlay of the structures of the FPA SPOC domain (cyan) and the Med25 ACID (gray).