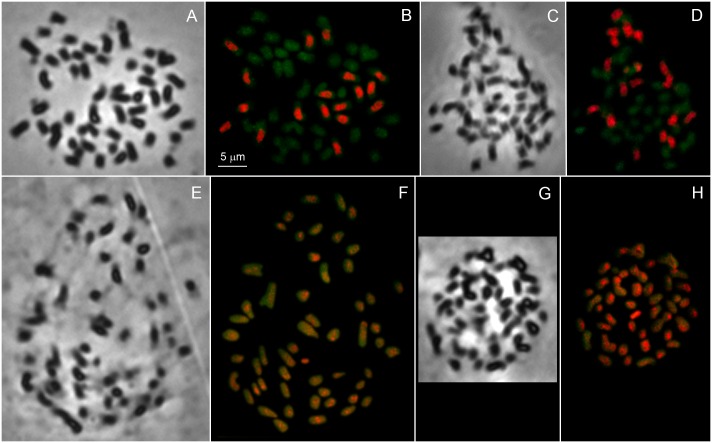
Fig 5. Genomic in situ hybridization on metaphase chromosomes of Chenopodium album s. str.
(A,B) Phase-contrast image of C. album s. str. chromosomes (accession 457/10) and GISH on the same metaphase plate with a probe consisting of total DNA of C. suecicum (accession 277/10, orange fluorescence) plus total DNA of C. strictum (accession 380/1, green fluorescence). (C, D) Phase-contrast image of C. album s. str. chromosomes (accession 457/10) and GISH on the same metaphase plate with a probe consisting of total DNA of C. ficifolium (accession 276/10, orange fluorescence) plus total DNA of C. strictum (accession 380/1, green fluorescence). (E, F) Phase-contrast image of C. album s. str. chromosomes (accession 457/10) and GISH on the same metaphase plate with a probe consisting of total DNA of C. strictum (accession 380/1, orange fluorescence) plus total DNA of C. album s. str. (accession 329/1, green fluorescence). (G, H) Phase-contrast image of C. album s. str. chromosomes (accession 329/1) and GISH on the same metaphase plate with a probe consisting of total DNA of C. striatiforme (accession 331/5, orange fluorescence) plus total DNA of C. album s. str. (accession 329/1, green fluorescence).