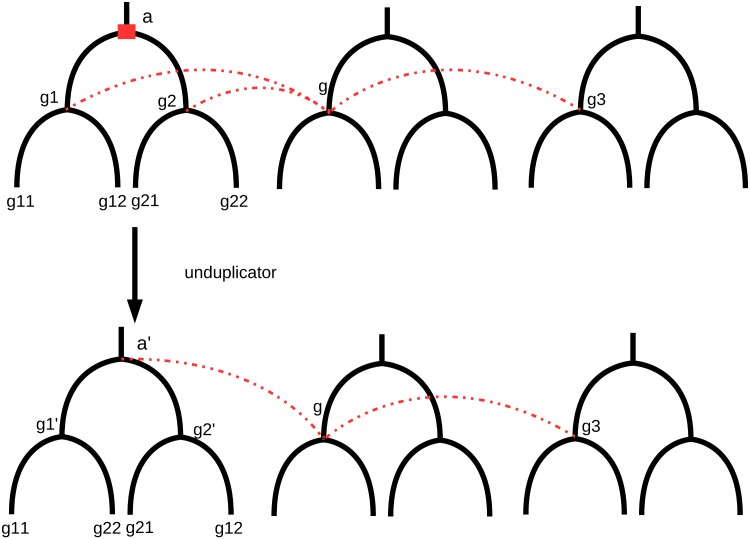
Fig 9. The unduplication principle (figure redrawn from [33]).
A non linearity is detected in an ancestral genome (gene g has three neighbors). Two of its neighbors g1 and g2 are issued from a possibly dubious duplication labeled node. The tree is rearranged so that its root is labeled with a speciation instead of a duplication. In the resulting configuration and are in two different species, so that g can have only one neighbor in this family, and linearity is recovered.