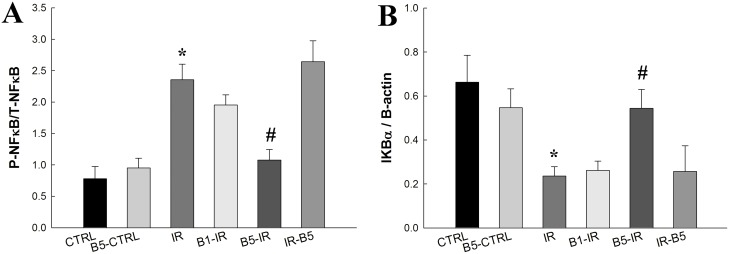
Fig 5. Preconditioning anti-VEGF antibody decreased IR-induced expression of NF-κB activation and nuclear translocation.
After IR, the (A) cytoplasmic level of phosphorylated NF-κB p65 was increased, whereas (B) IκB-α was significantly suppressed (both p<0.05). Preconditioning anti-VEGF antibody group (5mg/kg) restored IκB-α and reduced phosphorylated NF-κB p65 levels (both p<0.05). There was a significant difference from the * CTRL (p<0.05) and #IR (p<0.05) groups. Anti-VEGF antibody, anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody; IR, ischemia-reperfusion; ALI, acute lung injury; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; IκB-α, inhibitor of NF-κB alpha. CTRL, control group; B5-CTRL, control + preconditioning bevacizumab, 5mg/kg group; IR, ischemia-reperfusion group; B1-IR, IR + preconditioning bevacizumab, 1mg/kg group; B5-IR, IR + preconditioning bevacizumab, 5mg/kg group; IR-B5, IR + post-IR bevacizumab, 5mg/kg group.