Figure 1. Morphological (A,B,D) and electrical (C) measures showing that a combination of PEG solutions and PEG hydrogels can rapidly and completely repair (fuse, join together) cut axonal ends in vitro (A,C,D) and in vivo (B).
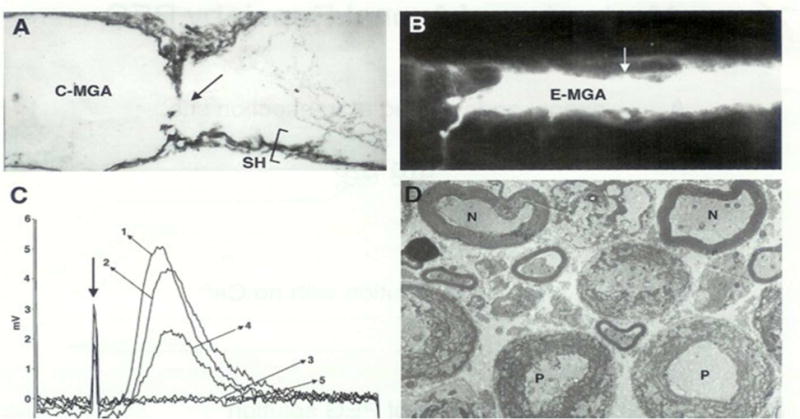
From Bittner at al., 2000 with permission.
A. Electron micrograph of a sagittal (longitudinal) section through a crayfish medial giant axon (C-MGA) PEG-fused in vitro that conducted action potentials (APs) intra-cellularly recorded through the fusion site (arrow) beginning within 10 minutes after PEG-fusion and continuing for 6 hours prior to fixation. Sh = cytoplasmic glial sheath of this un-myelinated axon.
B. Photomicrograph of a Lucifer dye-filled earthworm MGA (E-MGA) cut and PEG-fused in vivo 20 days prior to sampling. A PEG-based hydrogel was then applied to give mechanical strength in vivo. The E-MGA was completely repaired in vivo as evidenced by: (1) Its ability to conduct APs through the fusion site for 20 days; (2) These APs elicited all the behaviors evoked by intact E-MGAs in un-operated earthworms; (3) When this axon was then filled with fluorescein dye at 20 days post PEG-fusion, the dye filled the entire E-MGA which had same morphology as that shown by non-severed, control MGAs. Arrow = site of PEG-fusion of cut ends and site where the PEG-based hydrogel was applied.
C. Compound action potentials (CAPs) stimulated in one end chamber and recorded in the other end chamber of a three-chambered sucrose gap recording device. CAPs were first recorded from intact control bundles of rat spinal axons (trace labeled 1) prior to replacing the physiological saline in the central chamber with hypotonic Ca2+-free saline (trace labeled 2) at ~25° C. The spinal axons were then cut in the central chamber to completely eliminate the CAP (trace labeled 3). The cut ends were PEG-fused, and the central chamber was again perfused with calcium containing physiological saline. Within 15 minutes, CAPs were again recorded from PEG fused spinal axons (traces labeled 4). CAPs continued to be recorded for over 60 minutes before the experiment was terminated by again cutting the spinal axons in the central camber to eliminate the CAP, i.e., to demonstrate that the CAP was not an artifact (trace labeled 5).
D. Electron micrograph of cross sections of rat spinal axons at the site of PEG-induced fusion. APs conducted through the PEG-fusion site for 2 hours before fixation. N = PEG-fused axons of near normal morphology. P = PEG-fused axons of pathological morphology (disrupted myelin sheath and many membranous structures in the axoplasm).
