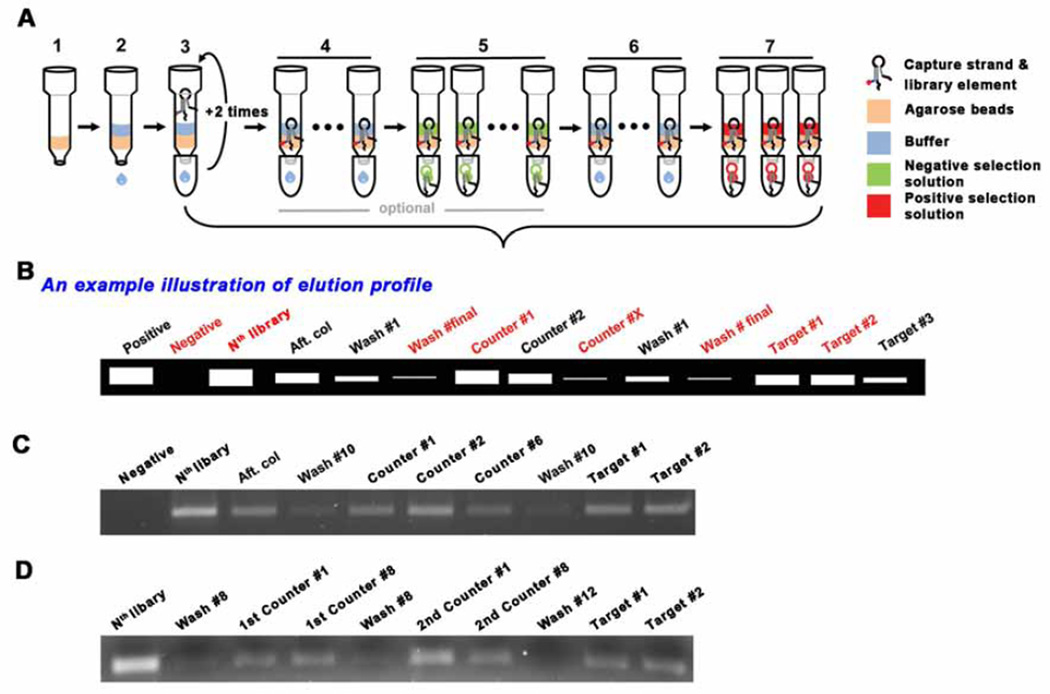
Fig. 2.
Schematic drawing for selection procedure. (A) (1) Agarose bead addition, (2) Wash the beads with SELEX buffer for equilbration, (3) Addition of the mixture of library and capture. After adding the mixture, the eluent is collected and re-applied into the column. This is to maximize the binding of the library-capture hybrid to the column. (4) Wash the column with the SELEX buffer ~10 times to remove uncaptured library elements. The number of washes can be adjusted based on the desired selection stringency. (5) Negative/Counter selection (optional). This elution step is to remove the less specific library elements that can bind to molecules which may compete with the desired target. (6) Additional wash - to remove residual solution from the negative selection, if applied. (7) Positive selection. During selection, several fractions need to be collected to monitor the elution profile. The choice of eluents to collect may be flexible, but the red labelled fractions should be collected, especially, the Nth library solution, the final buffer wash solution and the target solutions (#1 ~ #2). (B) An example illustration of elution profile. The collected eluents are compared though small scale PCR. The initial library templated PCR product can be utilized as a positive control for the PCR as well as the molecular weight marker. The commercial DNA ladder is used only when it is needed. The gel image of elution profile when one type of counter target is introduced (C), when two counter targets are applied (D).