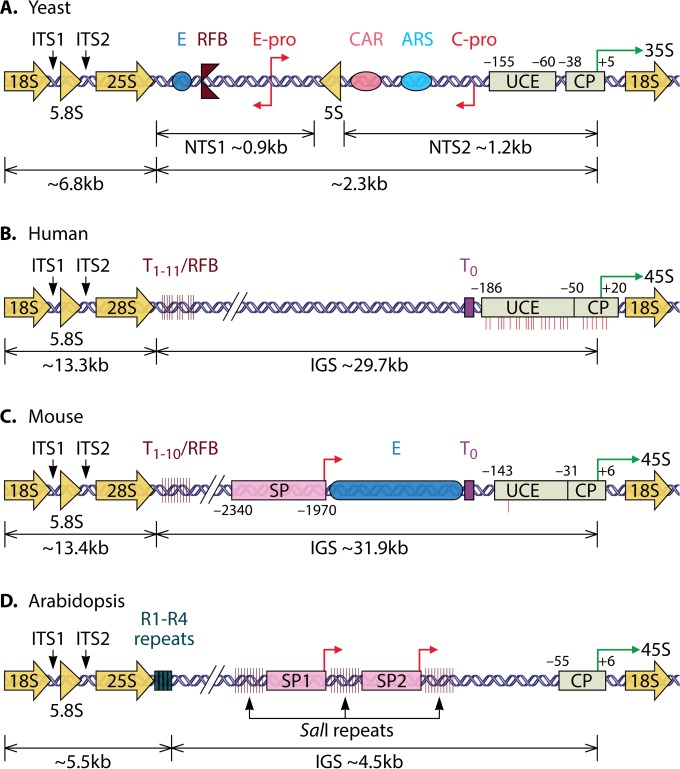
FIG 1.
rDNA structures in yeast, human, mouse, and Arabidopsis. The graphic of the yeast rRNA gene is derived from data reported under GenBank accession no. U53879, and graphics of human rRNA and mouse genes are derived from data reported under accession no. U13369 and BK000964, respectively. A graphic of the Arabidopsis rRNA gene is shown, as reported previously (11, 13, 197, 198). (A) In yeast, a single unit of rDNA (9.1 kb) consists of 5S, 5.8S, 18S, and 25S transcribed genes; internal transcribed spacers (ITS1 and ITS2); and two NTSs, NTS1 and NTS2. The repetitive sequences of rDNA undergo recombination, which consequently leads to genomic instability (199). In contrast, as the integrity and the proper function of the rDNA repeats play important roles in cell viability, rDNA recombination is generally repressed in a manner that is dependent on Sir2 (153). The yeast rDNA promoter consists of a core promoter (CP) and an upstream control element (UCE). The green arrow indicates the transcription start site (TSS) of the pre-rRNA. All nucleotide numbers are relative to the first nucleotide of the TSS (position +1). The enhancer element (E) and RFB are located near the 3′ end of the 25S rDNA in NTS1. The cohesin-associated region (CAR) and ARS are found in NTS2. RNAPII transcription of rDNA starts from two promoters, called cryptic RNAPII promoter (C-Pro) and EXP promoter (E-Pro). The intergenic cryptic transcripts are produced from C-Pro and E-Pro (200). (B and C) Human rDNA (43 kb) and mouse rDNA (45.3 kb) consist of 5.8S, 18S, and 28S transcribed genes; ITS1 and ITS2; and a long NTS called an IGS (intergenic spacer). The IGSs include multiple regulatory elements: the rDNA promoter (CP and UCE), an enhancer element (E), and upstream (T0) and downstream (T1 to T11 in human and T1 to T10 in mouse) terminators. A spacer promoter (SP) is found in the mouse IGS (201, 202). TTF-I is a transcription factor that recognizes and binds to the upstream terminator (T0) and downstream terminators to facilitate the recruitment of the NoRC or NuRD complex to the rDNA promoter (203). In mouse, DNA methylation occurs in a single CpG dinucleotide in the UCE position at position −133 relative to position +1, as shown by a red line below the UCE, while in humans, there are ∼25 CpG sites of DNA methylation in the promoter region (58, 181). (D) Arabidopsis rDNA (∼10 kb) consists of 5.8S, 18S, and 25S transcribed genes; ITS1 and ITS2; and an IGS. The Arabidopsis IGS region is composed of a gene promoter sequence (positions −55 to +6); two SPs, SP1 and SP2; and three SalI repeats. Four repeat sequences, R1 to R4, are located downstream of 25S rDNA in the 3′ external transcribed spacers (11, 13, 197, 198). In the Arabidopsis ecotype Col-0, four distinct rRNA gene variants, VAR1, VAR2, VAR3, and VAR4, are identified based on variations within R1 to R4. No UCE equivalent to yeast or mammalian UCEs has been identified in the Arabidopsis rDNA promoter.