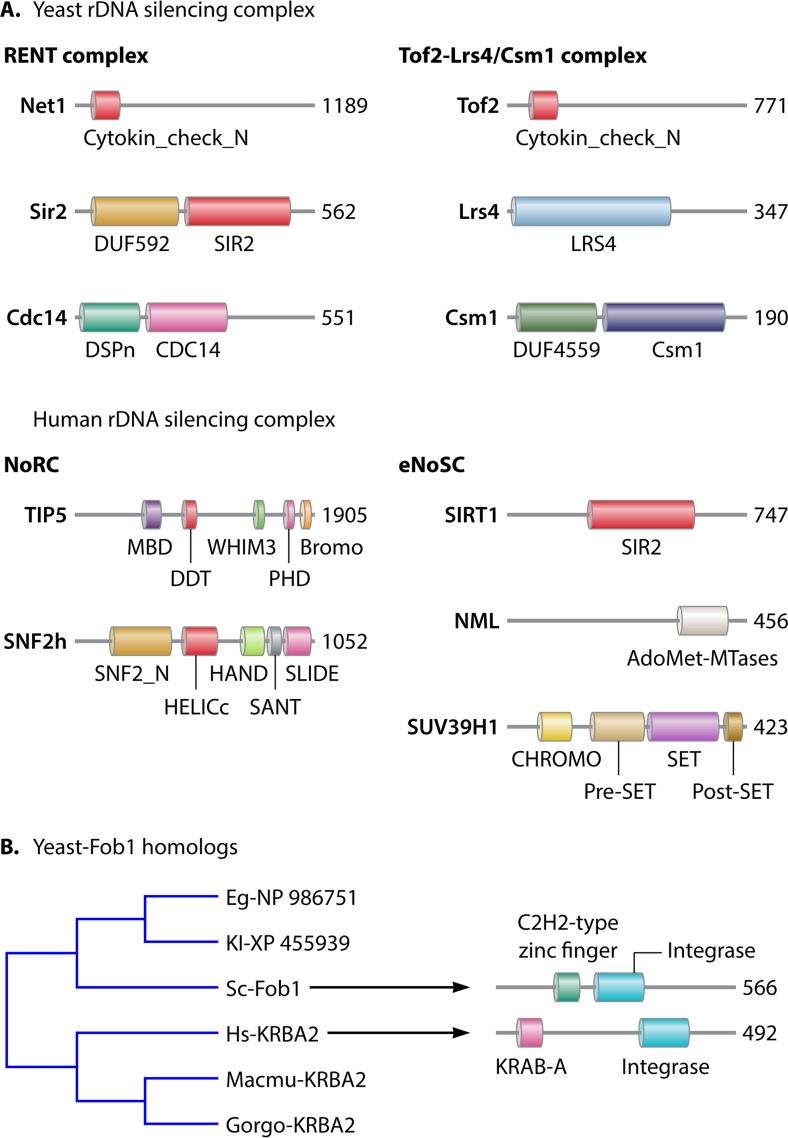
FIG 2.
rDNA-silencing components in yeast and mammals. (A) Two main rDNA-silencing complexes, RENT and Tof2-Lrs4/Csm1, are found in yeast. The RENT complex is composed of Net1, Sir2, and Cdc14 proteins. Human and mouse NoRCs are composed of TIP5 and SNF2h, while the eNoSC is composed of SIRT1, NML, and SUV39H1 (only the domain organization of human NoRC and eNoSC components is represented). Cytokin_check_N, Cdc14 phosphatase-binding protein N terminus; SIR2, silent information regulator 2; LRS4, loss of rDNA-silencing protein 4; DSPn, dual-specificity protein phosphatase, N-terminal half; CDC14, cell division control protein 14; Csm1, chromosome segregation in meiosis protein 1; MBD, methyl-CpG-binding domain; DDT, DNA-binding homeobox and different transcription factors; WHIM3, WSTF, HB1, Itc1p, and MBD9 motif 3; PHD, plant homeodomain; Bromo, bromodomain; AdoMet-MTases, S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferases; SNF2_N, SNF2 family N-terminal domain; HELICc, helicase conserved C-terminal domain; SANT, SWI3, ADA2, N-CoR, and TFIIIB; SLIDE, SANT-like ISWI domain; CHROMO, chromatin organization modifier; SET, Su(var)3-9 enhancer-of-zeste trithorax; DUF, domain of unknown function. (B) Homologs of yeast Fob1 in fungi and mammals. NCBI Blast analysis using yeast Fob1 protein sequences shows homology to human KRBA2. The sequences are derived from data reported under accession numbers XP_455939 for Kl, NP_986751 for Eg, NP_010395 for Sc, NP_998762 for Hs, XP_004058617 for Gorgo, and XP_001113012 for Macmu. Kl, Kluyveromyces lactis; Eg, Eremothecium gossypii; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Hs, Homo sapiens; Gorgo, Gorilla gorilla; Macmu, Macaca mulatta. Fob1 consists of a C2H2-type zinc finger motif and an integrase catalytic core-like structure (204). Human KRBA2 is a zinc finger protein of the C2H2 family and contains Krüppel-associated box A (KRAB-A) and integrase core domains.