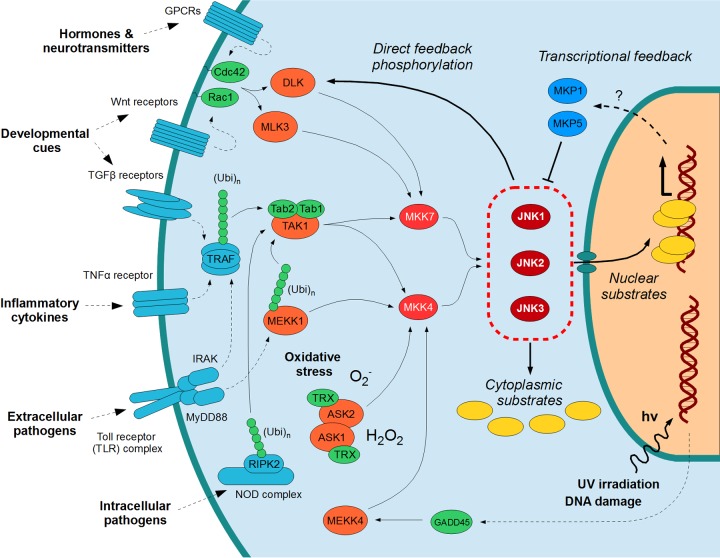
FIG 1.
Overall organization of JNK signaling pathways. JNK pathways are activated by a variety of extracellular stimuli (e.g., cytokines, pathogens, morphogenic factors, hormones) as well as intracellular stimuli (e.g., oxidative stress, DNA damage), converging on the three JNKs. These phosphorylate a variety of cytoplasmic as well as nuclear substrates and engage in direct (e.g., phosphorylation of MAP3Ks) as well as indirect (e.g., expression of the dual-specificity phosphatases MKP1 and MKP5) feedback circuits. The protein kinase members of the core MAPK pathway are displayed in red, while critical proteins directly controlling MAP3K activation are shown in green. Proteins further upstream of the pathway are colored turquoise, MKPs are blue, and substrates are yellow. Note that, for the purposes of clarity, not all the known proteins or possible pathways are shown here. Continuous arrows imply direct binding or direct enzymatic reactions, while dotted arrows show either indirect, multistep reactions or connections where the exact mechanism(s) is uncertain. Abbreviations (other than the protein names defined in the main text): GPCR, G-protein-coupled receptor; Ubi, ubiquitin (usually nondegradative, with Lys63 linkage).