Fig. 2.
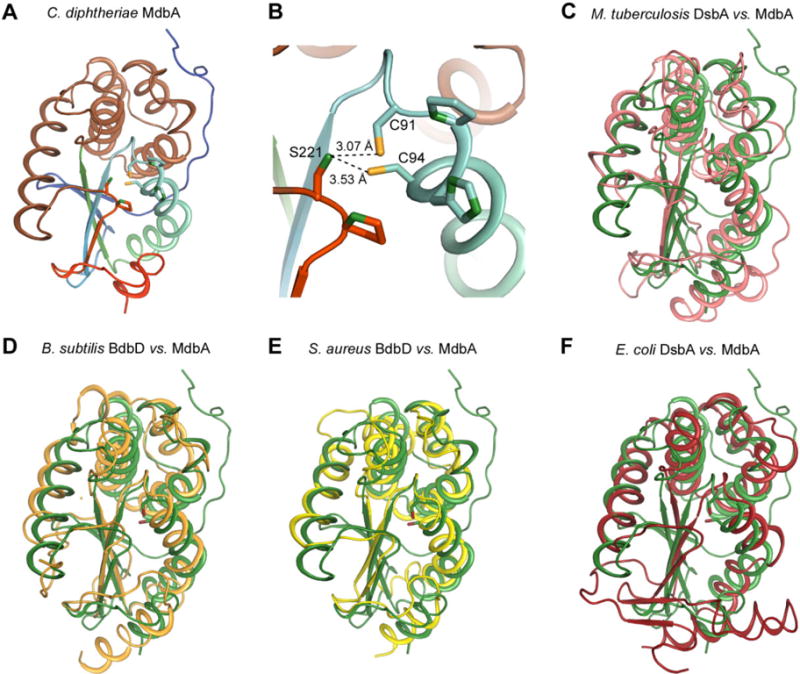
Structural analysis of the C. diphtheriae disulfide bond-forming protein MdbA.
A. The C. diphtheriae MdbA crystal structure (residues 43–244), solved to a 1.77-Å resolution, possesses a thioredoxin-like domain (rainbow colors) and an alpha-helical domain (light brown).
B. The MdbA active site is comprised of C91, P92, H93 and C94. The Sγ group in the two cysteine residues forms a hydrogen bond with S221 of the Cis-Pro element.
C–F. The MdbA structure (green) was aligned with M. tuberculosis DsbA (C; PDB: 4K6X), B. subtilis BdbB (D; PDB:3EU3), S. aureus DsbA (E; PDB:3BCI) and E. coli DsbA (F; PDB:1A2L).
