Figure 4.
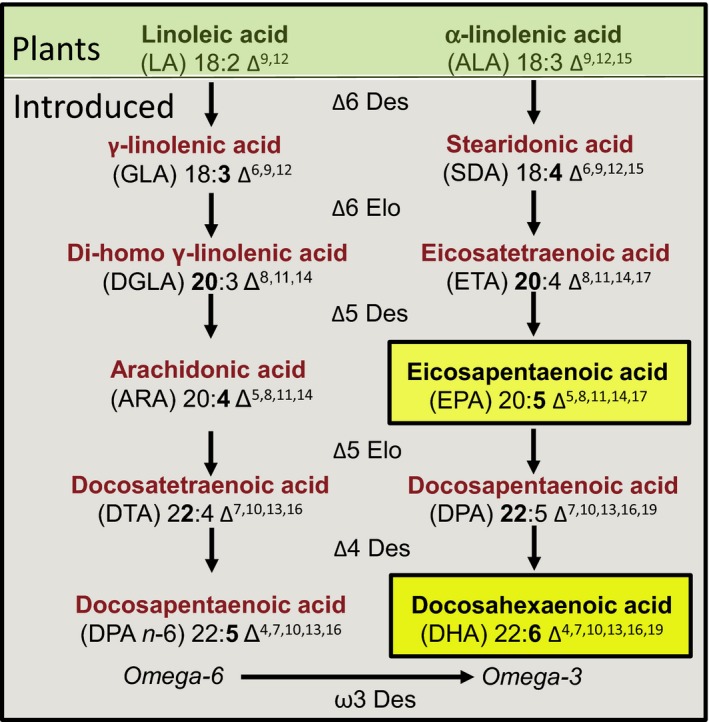
A representation of the Δ6‐pathway for biosynthesis of long‐chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in plants.
The substrates linoleic acid (LA) and α‐linolenic acid (ALA) (highlighted in the box at the top) are sequentially converted through the combined activity of separate desaturase (Des) and elongase (Elo) to the target long‐chain omega‐3 fatty acids – eicosopentanoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Additional enzymes with omega‐3 desaturase (ω3 Des) activities are also included to enhance the production of EPA and DHA over omega‐6 forms such as arachidonic acid (ARA) via the generic conversation of omega‐6 to omega‐3. An alternative configuration of the pathway (not illustrated) begins with a Δ9‐elongation and two rounds (Δ8, Δ5) of desaturation to generate ARA and EPA.
