Figure 2.
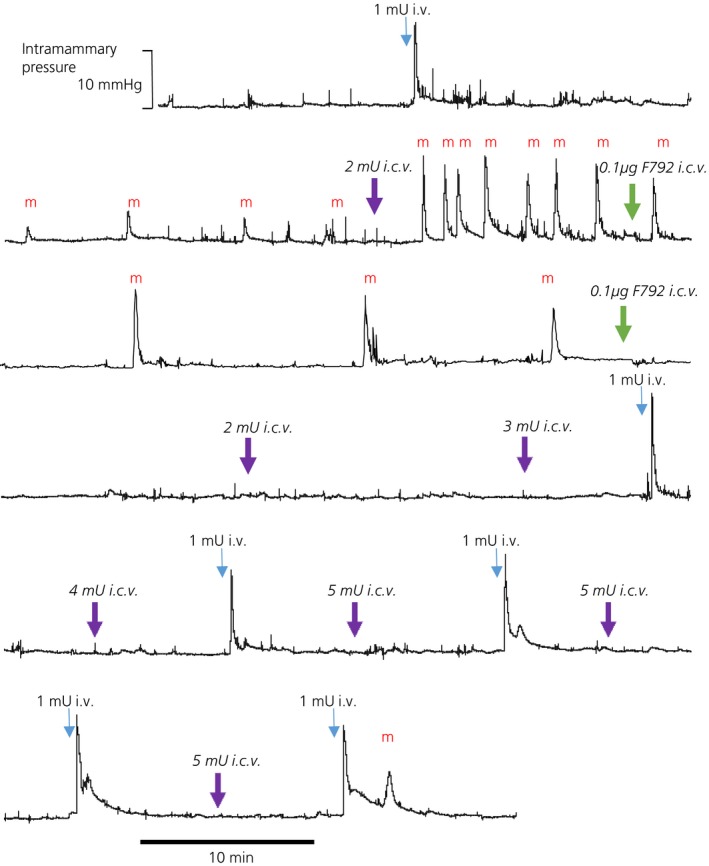
Intramammary pressure recording in a urethane‐ anaesthetised lactating rat (day 11/12, litter of 10 pups) at least six pups suckling throughout: the trace is a continuous recording. A bolus i.v. dose of 1 mU oxytocin demonstrated mammary gland sensitivity to oxytocin, and, in response to the suckling stimulus, reflex milk ejections (m) were observed. Oxytocin (2 mU) given i.c.v. triggered a sequence of 8 large milk ejections a few minutes apart. After an i.c.v. infusion of 0.1 μg F792 three further milk ejections were seen, but after a second i.c.v. infusion of 0.1 μg F792 no further spontaneous milk ejections were observed, even after i.c.v. infusions of 2, 3, 4, and 5 mU oxytocin. Bolus i.v. doses of 1 mU oxytocin elicited sharp increases in intramammary pressure similar to the initial response, showing intact sensitivity of the mammary gland to oxytocin. About 90 min after the second injection of F792 one small spontaneous milk ejection (m) was observed.
