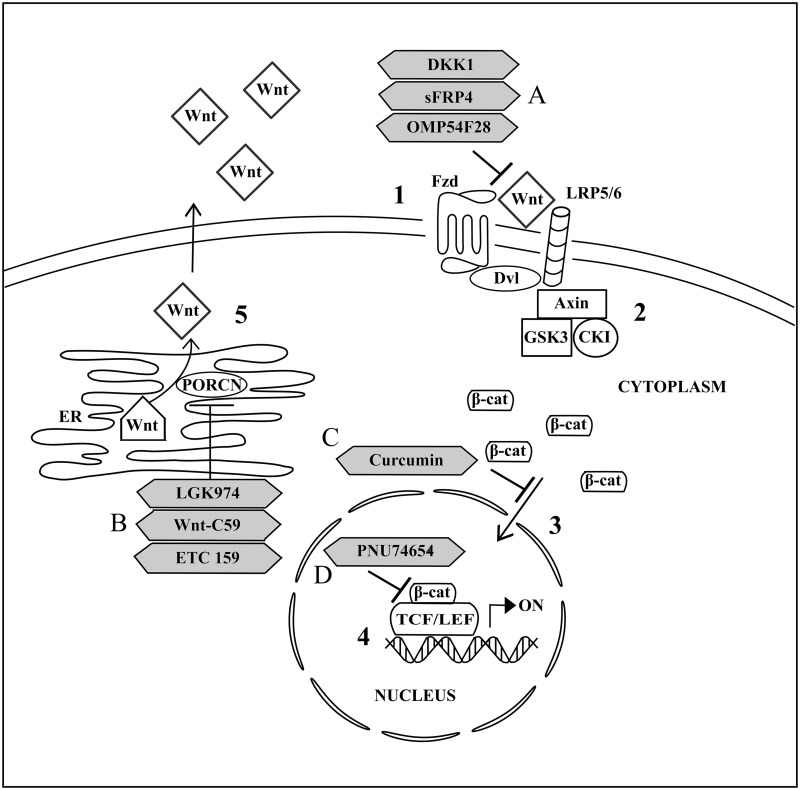
FIGURE 2.
Activated canonical Wnt signaling pathway and the drug targeted components. (1) Signal transduction is activated upon binding of Wnt from outside the cell to Fzd and LRP 5/6 at the cell membrane. (2) Dvl and subsequently Axin, GSK3, CK1 are recruited to the cell membrane and thus inhibiting the formation of multiprotein destructive complex. (3) Accumulated cytoplasmic β-catenin is further translocated into nucleus. (4) Transcription of Wnt targeted genes is activated upon binding of nuclear β-catenin to TCF/LEF. (5) Wnt palmitoylation and secretion to outside of the cell is facilitated by PORCN in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). (A) OMP54F28 and sFRP4 are antagonists for Wnt and Fzd interaction while DKK1 antagonizes Wnt/β-catenin signaling through binding to LRP 5/6. (B) LGK974, Wnt-C59, and ETC 159 are inhibitors for PORCN activities. (C) Curcumin acts as an inhibitor for nuclear translocation of cytoplasmic β-catenin. (D) PNU74654 functions as an inhibitor for interaction nuclear β-catenin with TCF/LEF.