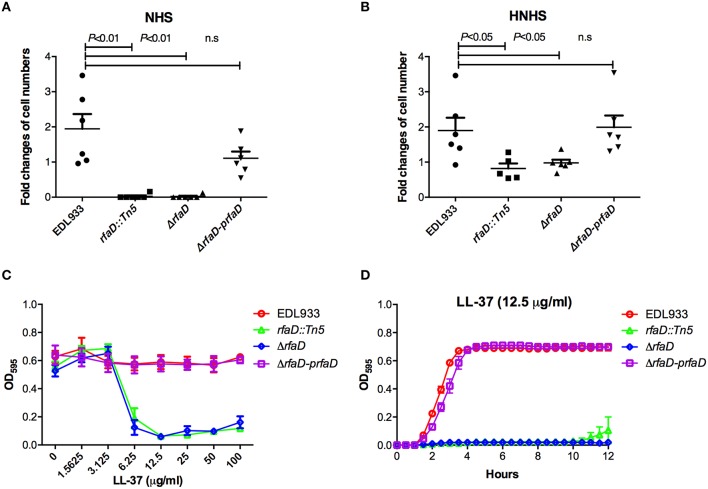
Figure 6.
Deletion of EHEC rfaD increases its susceptibility to human serum killing and the antimicrobial peptide LL-37. The fold changes of bacterial cell numbers of wild-type EDL933, EDL933 rfaD::Tn5, EDL933:ΔrfaD and EDL933:ΔrfaD-prfaD after incubation in 10% normal human serum (NHS) (A) or 10% heat-inactivated normal human serum (HNHS) (B) at 37°C for 60 min were measured. Experiments were conducted independently at least three times, and error bars indicate the standard deviations. (A) The rfaD transposon mutant (rfaD::Tn5, P = 0.001) and rfaD deletion mutant (ΔrfaD, P = 0.001) showed significant decreased survival ratio compared to that of wild-type EDL933 (EDL933) in 10% NHS. The rfaD complement bacteria (ΔrfaD-prfaD) showed comparable survival ratio compared to that of EDL933 (P = 0.101) in 10% NHS. (B) The rfaD transposon mutant (rfaD::Tn5, P = 0.031) and rfaD deletion mutant (ΔrfaD, P = 0.034) showed significantly decreased survival ratio compared to that of wild-type EDL933 (EDL933) in 10% HNHS. The rfaD complement bacteria (ΔrfaD-prfaD) showed comparable survival ratio compared to that of EDL933 (P = 0.854) in 10% HNHS. n.s. indicates no statistical significance. (C) The OD595 values of wild-type EDL933 (EDL933), EDL933 rfaD::Tn5 (rfaD::Tn5), EDL933:ΔrfaD (ΔrfaD), and EDL933:ΔrfaD-prfaD (ΔrfaD-prfaD) cultured with different dose of LL-37 at 37°C for 16 h were monitored. (D) The growth curves of EDL933, rfaD::Tn5, ΔrfaD and ΔrfaD-prfaD in the presence of 12.5 μg/ml LL-37 at 37°C.