Figure 1.
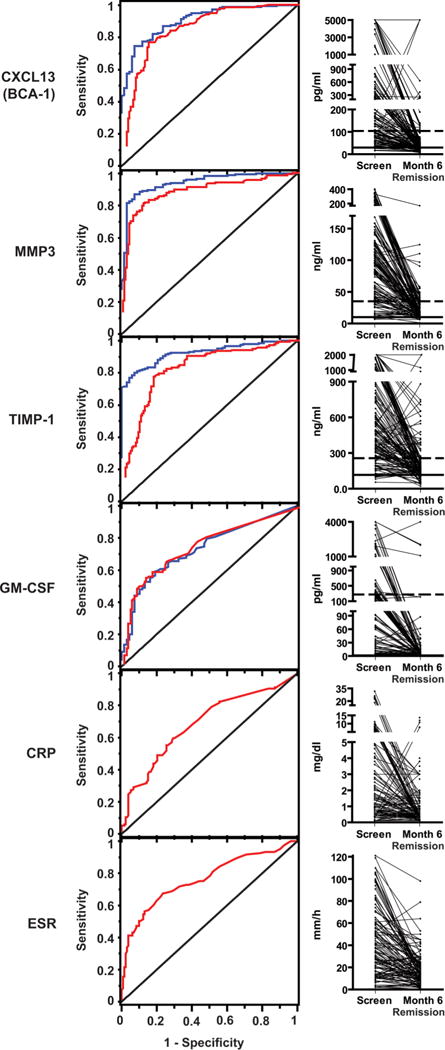
Levels of selected markers in severe active ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), AAV in remission, and in healthy controls. Left panels: receiver operating characteristic curves showing the ability of selected markers to distinguish severe active AAV (at screening) from remission at month 6 (blue curves), and severe active AAV from healthy controls (red curves). The diagonal line indicates what would be expected with no discrimination between groups. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein were not measured in healthy controls. Right panels: levels in individual patients. All subjects had severe active AAV at screening and were in remission at month 6. The medians and 95th centiles among healthy controls are shown with horizontal solid and dotted lines, respectively. CRP, C-reactive protein; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; GM-CSF, granulocyte–monocyte colony-stimulating factor; MMP3, matrix metalloproteinase-3; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1.
