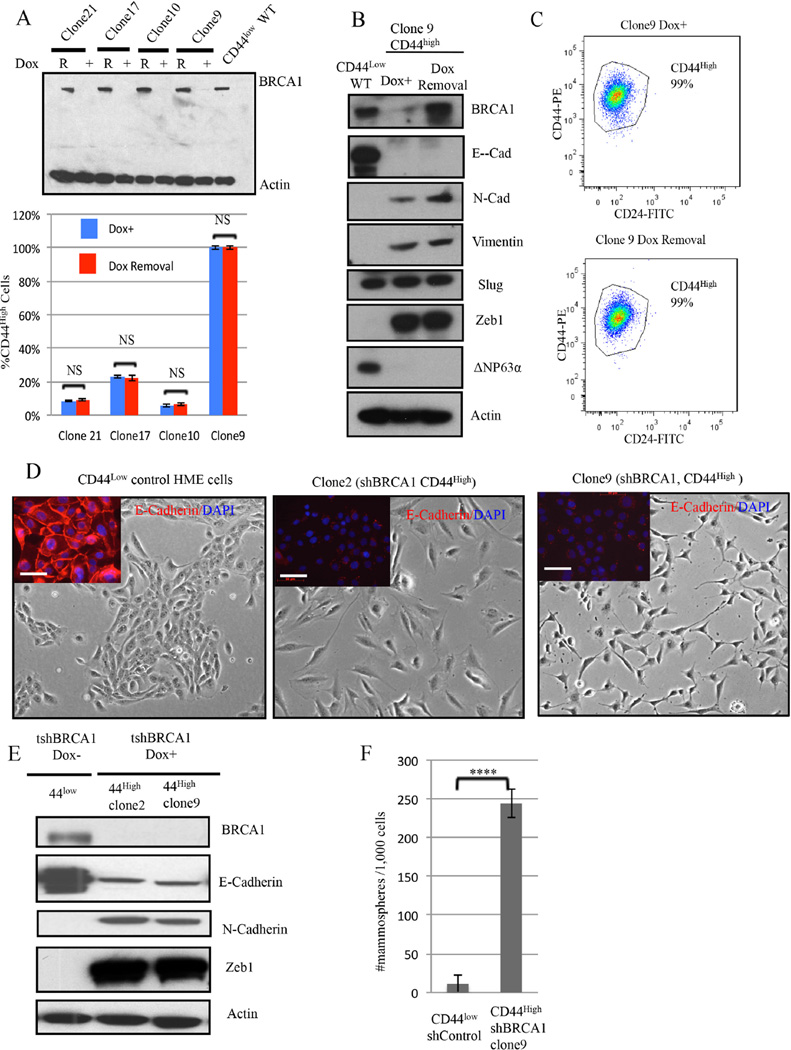
Figure 2. Aberrant differentiation of HME cells following BRCA1 depletion.
2A) (Top panel) Immunoblotting for BRCA1 after Doxycycline-induced BRCA1 depletion (DOX +) and after BRCA1 re-accumulation (R) for 4 weeks after Dox removal. (Lower panel)The abundance of CD44high cells was measured before and 4 weeks after doxycycline removal in four, independent, BRCA1- depleted clones. The data represented are mean values ±S.D. NS: Not significant.
2B) Immunoblotting for BRCA1 and EMT markers in CD44high HME cells (clone9) after BRCA1 depletion or reexpression.
2C) Representative CD24 and CD44 FACS profiles of clone 9 derived after BRCA1 depletion (clone 9 Dox+) and 4 weeks after subsequent Doxcycline removal.
2D) Respective phase-contrast images of CD44low parental and of CD44high cells (clones 2 and 9) isolated after Dox-induced BRCA1 depletion in CD44low cells. The inserts depict the results of anti-E-cadherin (red) and DAPI (blue) staining. Scale bar: 50 µm
2E) Immunoblotting for EMT marker proteins in two, independent, aberrantly differentiated CD44high clones (clones 2 and 9) that appeared after BRCA1 depletion in CD44low cells. 2F) Mammosphere assays were performed on a clone (clone9) containing uniformly CD44high HME cells derived after BRCA1 depletion of CD44low cells or on shluc CD44low control cells. The data are represented as mean values ±S.D. ****P<0.0001.