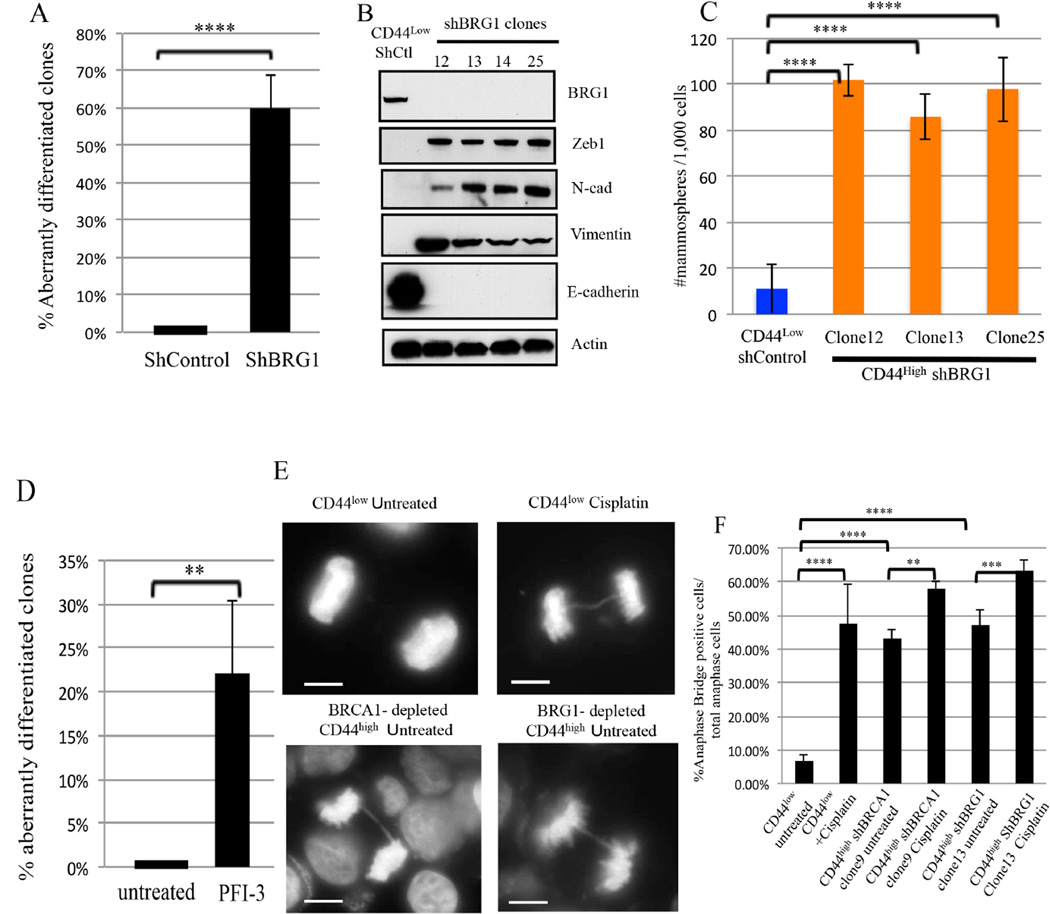
Figure 4. BRG1 suppresses DNA damage-associated aberrant differentiation (Also see Figures S3 and S4).
4A) Summary of the effect of BRG1 depletion on the differentiation state of CD44low HME cells. ****P<0.0001.
4B) Immunoblotting for EMT markers from four, independent CD44high clones following BRG1 -depletion.
4C) Mammosphere assays were performed on CD44high HME cells that appeared after BRG1 depletion and on Shluc CD44low control cells. The data represented are mean±S.D. ****P<0.0001.
4D) Summary of the BRG1 inhibitor, PFI-3 (50 µM), exposure on the differentiation state in CD44low HME cells. . The data represented are mean values ±S.D. **P<0.01. **P<0.01. 4E) Representative images of normal anaphase chromosomes and anaphase bridges in untreated and cisplatin-treated (1µM, 24hr) CD44low cells, respectively. Other panels depict drug-free CD44high cells following long term, hairpin-mediated BRCA1 (clone 9) or BRG1 (Clone 13) depletion. Scale Bar: 10 µM.
4F) Analysis of anaphase bridge-positive cells in drug-free CD44low, shBRCA1 clone 9, and shBRG1 clone 13 CD44high cells and after exposure of these cells to cisplatin (1 µM, 24 hours). The data represented are mean±S.D.