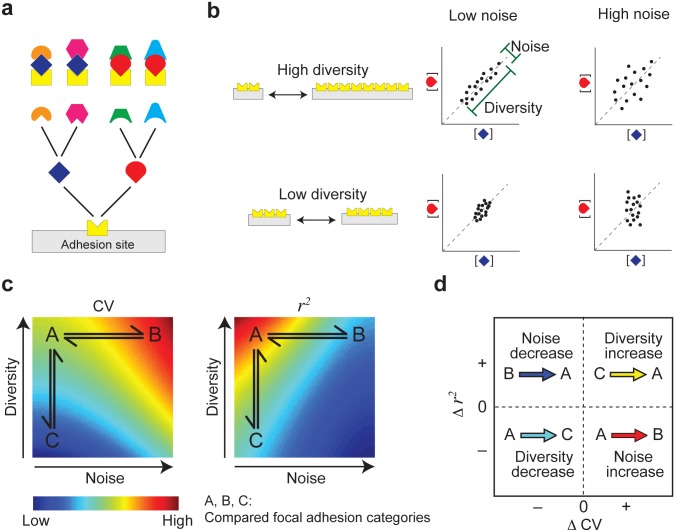
Fig 2. Inferring changes in noise levels in the molecular content of focal adhesions.
(a) An assembly process with competing binding interactions. (b) Higher diversity in the local levels of a recruiting protein leads to a stronger correlation between the recruited proteins, while higher noise causes the opposite. (c) Simulated CV and r2 of the densities of the dark-blue and red components as a function of binding noise and diversity in the density of the yellow component among focal adhesions. (d) Inferring changes in noise levels based on ΔCV and Δr2. Changes between focal adhesion categories exemplified in (c) are indicated. The inference approach was validated by systematic screen of diversity and noise levels for competitive and non-competitive assembly processes.