Fig. 3. Super-resolution optical imaging through the TiO2 mSIL.
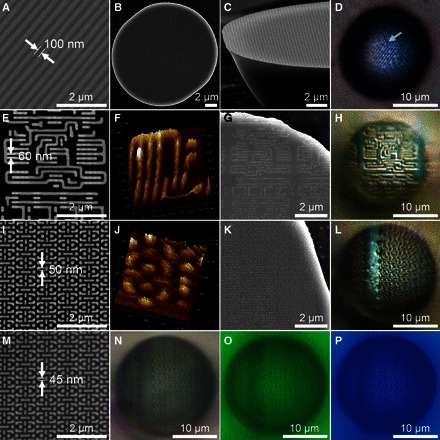
(A to P) SEM images of a Blu-ray disk containing 100-nm-wide grooves (A) and the wafer patterns with 60-nm (E), 50-nm (I), and 45-nm pitches (M) after gold coating of sample (I). (B) and (C), (G), and (K) are the bottom surfaces of the mSIL detached from the surface of samples (A), (E), and (I), respectively. AFM images of the wafer pattern with 60-nm (F) and 50-nm pitches (J). Optical microscopy images of the TiO2 mSIL focused on the surface of a Blu-ray disk (D) and wafer patterns with 60-nm (H), 50-nm (L), and 45-nm pitches (N to P), with magnification factors of 1.8, 3.1, 3.0, and 3.1, respectively. The last mSIL was illuminated under white light (N), green light (λ ~ 540 nm) (O), or blue light (λ ~ 470 nm) (P). The mSIL had widths of about 20 μm.
