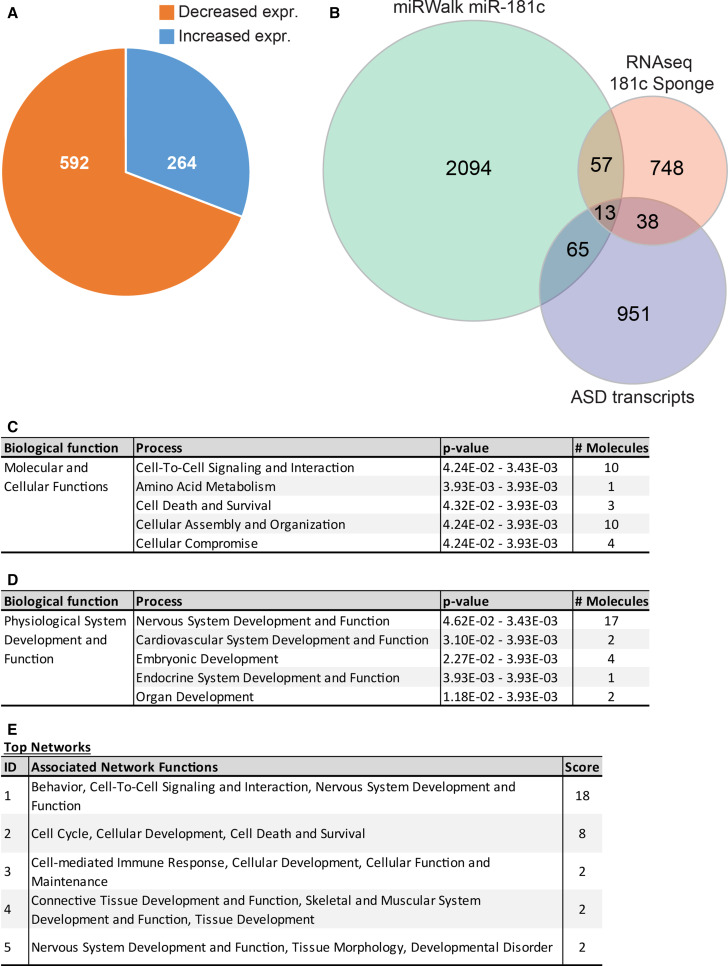
Fig. 1.
Inhibition of miR-181c function alters the expression of genes functionally involved with neurodevelopmental processes. a Pie diagram depicts the number of genes significantly (p < 0.05) increased (blue) and decreased (orange) in expression by more than 1.2 fold. b Venn diagram shows the overlap between the putative miR-181c targets identified with miRWalk (2229 molecules), the significantly altered transcripts after miR-181c inhibition using the sponge in cortical neurons (786 molecules) and significantly altered transcripts identified in cortical material from ASD patients (1067 molecules). This analysis resulted in the identification of 70 significantly altered transcripts containing a miR-181c binding site and 13 of which previously found to be dysregulated in ASD. c, d Overview of the gene ontology study shows 70 genes containing a miR-181c binding site in their 3′UTR, altered in their levels upon inhibition of miR-181c. c The most significant process in the category molecular and cellular functions is cell-to-cell signaling and interaction. d Within the category physiological system development and function the process nervous system development and function has the highest number of dysregulated genes. e A list of the top five highest scoring gene networks identified by the IPA. Each individual network has functions assigned to them with the highest scoring network involved in behavior, cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, nervous system development and function