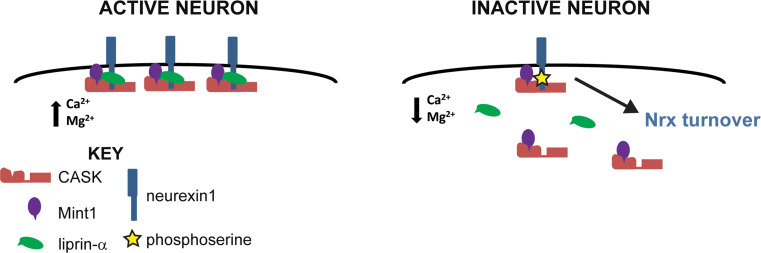
Fig. 8.
Model of neurexin stabilization by CASK. In active neurons, when levels of divalent ions are high, neurexin is stabilized by its interaction with CASK and its binding partners. In inactive neurons, when levels of divalent ions decrease, thus activating CASK’s kinase activity, CASK phosphorylates neurexin (yellow star), which disrupts liprin’s interaction with the complex and results in an increase in neurexin turnover. CASK, red; Mint1, purple; liprin-α, green; neurexin, blue