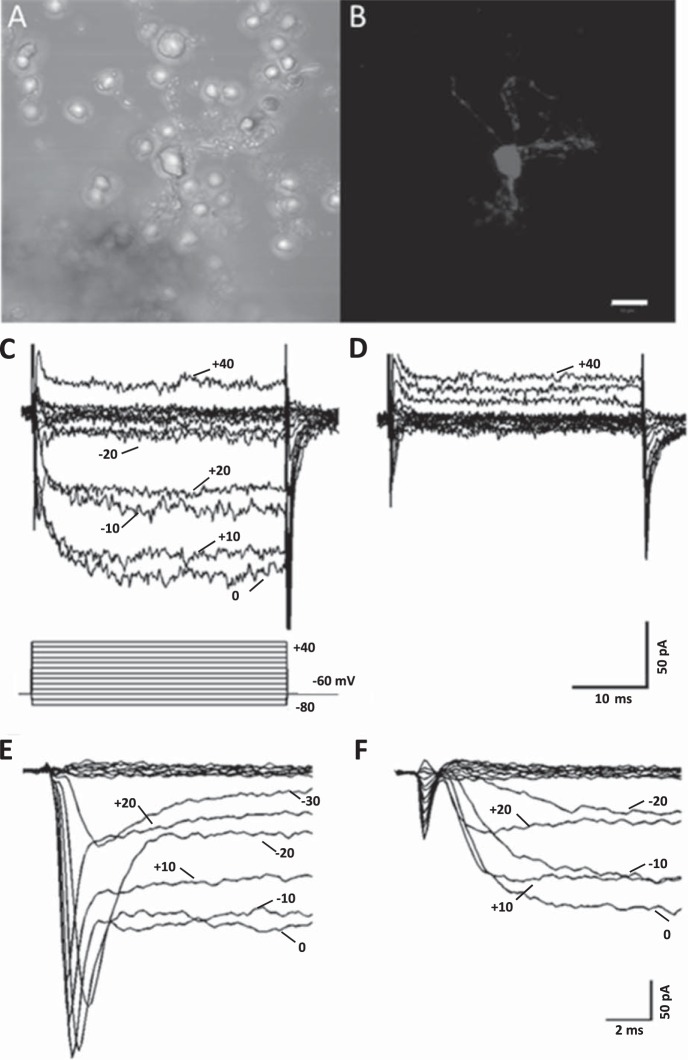
Fig. 1.
Ca channel currents in an isolated horizontal cell from a connexin-57-iCre × ROSA26-tdTomato (Cx57-tdTomato) mouse retina. A: phase-contrast image of an enzymatically treated, isolated horizontal cell. B: same field of view under green excitation light (560 nm) with red emission filter (610 nm), showing red tdTomato fluorescence from cell body and surrounding cellular processes. Scale bar for both images is 10 μm. C: inward Ca channel currents carried by Ba2+ recorded in response to the voltage step paradigm shown below traces. Cell was voltage-clamped at a holding potential of −60 mV, and steps lasting 40 ms were applied to potentials from −80 mV to 40 mV in 10-mV increments. D: same cell as in C shows that Ca channel currents were completely blocked during superfusion with 10 μM Cd2+. E: Na channel currents and Ca channel currents in response to voltage clamp steps from −80 to +20 mV, shown on an expanded timescale and from a different cell. F: same cell as in E showing 100 nM TTX blocking the Na channel currents.