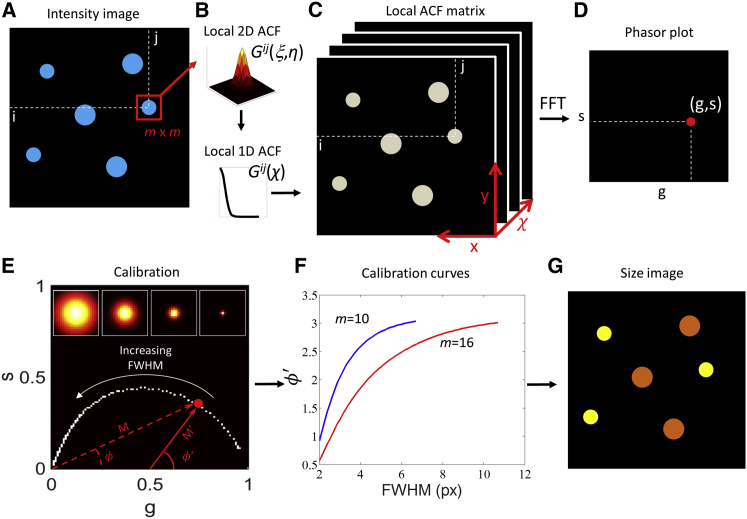
Figure 1.
(A–F) Schematic workflow of the PLICS method. A small m × m region around each pixel (i,j) of an intensity image (A) is used to calculate a local 2D spatial correlation function (B, top) and its angular mean (B, bottom), which is stored along the third dimension in the corresponding (i,j) position of the local ACF matrix (C). (D) The phasor coordinates (g,s) are obtained by performing an FFT along the third dimension of the local ACF matrix in the (i,j) point (C). (E) Phasor plot obtained by a collection of calibration structures, examples of which are shown in the inset, from which mask-specific calibration curves are obtained (F) and used to construct a size image (G). To see this figure in color, go online.