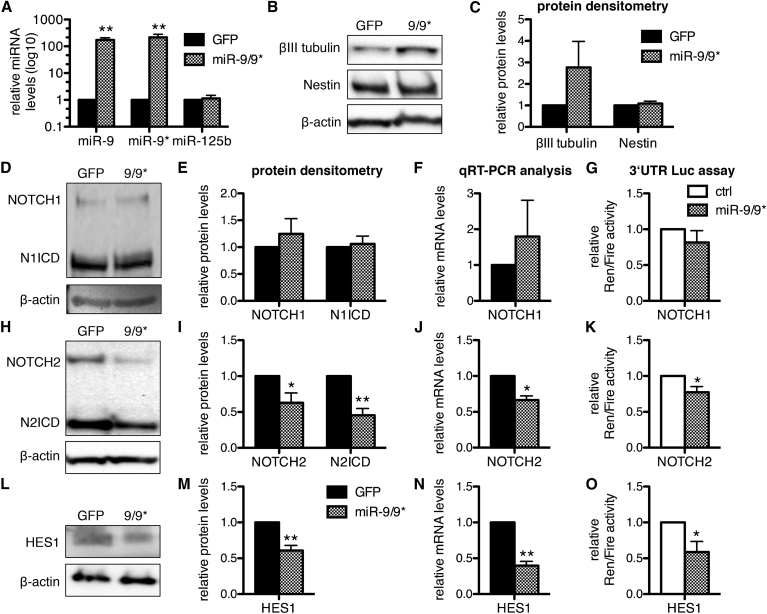
Figure 1.
miR-9/9∗ Target NOTCH2 and HES1
(A) qRT-PCR analyses of miR-9, miR-9∗, and miR-125b in lt-NES cells overexpressing the miR-9-1 genomic sequence (9/9∗) or GFP (used as control) after 4 days of doxycycline treatment. Data are normalized to miR-16 reference levels and presented as average changes + SEM relative to expression in GFP-expressing lt-NES cells (GFP, equal to 1; n ≥ 3; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, Student's t test).
(B, D, H, L) Representative western blot analyses of βIII-tubulin and Nestin (B), full-length NOTCH1 (D), NOTCH2 (H), and their respective intracellular domains (ICD), as well as HES1 (L) protein levels in I3 lt-NES cells overexpressing the miR-9/9∗ locus induced by 4 days of doxycycline treatment compared with a GFP control construct (n ≥ 3). β-Actin is shown as loading control.
(C, E, I, M) Corresponding densitometric analyses of βIII-tubulin and Nestin (C), NOTCH1 and N1ICD (E), NOTCH2 and N2ICD (I), and HES1 (M) protein levels normalized to β-actin. Data are presented as mean ± SEM relative to expression in I3 lt-NES cells overexpressing GFP (equal to 1; n ≥ 3; ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, Student's t test).
(F, J, N) qRT-PCR analyses of NOTCH1 (F), NOTCH2 (J), and HES1 (N) transcript levels in the conditions described above. Data are normalized to 18S rRNA reference levels and presented as average changes + SEM relative to expression in lt-NES cells overexpressing GFP (equal to 1; n = 6; ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, Student's t test).
(G, K, O) Analyses of luciferase activity in I3 lt-NES cells expressing the 3′ UTRs of NOTCH1 (G), NOTCH2 (K), and HES1 (O) cloned downstream of Renilla (Ren) luciferase and transfected with synthetic mimics for miR-9 and miR-9∗ (9/9∗) or a short RNA scrambled control (ctrl). Data are normalized to firefly (Fire) luciferase activity and presented as average changes + SEM relative to activity in I3 lt-NES cells transfected with the scrambled control (ctrl, equal to 1; n = 5; ∗p ≤ 0.05, Student's t test). All experiments were performed in I3 lt-NES cells cultured under self-renewing conditions, i.e., in the presence of EGF and FGF2.