Fig. 1.
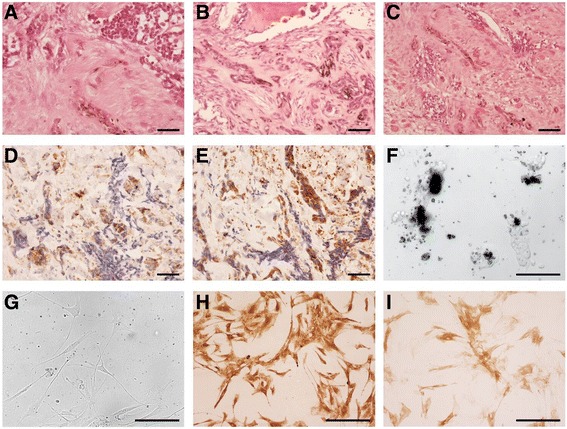
Pathological characterization of the MNTI tumor. The two main tumor cell types are readily apparent following haematoxylin and eosin-stained section from the tumor: (a) nests of small round cells with scant cytoplasm and hyperchromatic nuclei (top) and cords of polygonal, ‘epithelial-like’ cells containing speckles of melanin (bottom center), (b) Scattered pigment-containing tumor cells in bone, (c) MNTI tumor cells in soft tissue with residual muscle fibers evident. Tumor cells stain positive for CD99 (d) and HMB45 (e). f Bright field images of the cell line derived from the MNTI at passage 2 produced copious amounts of melanin causing cell clumps to appear black. g Phase contrast image of passage 6 of the cell line no longer synthesized melanin and the cells had adopted a more fibroblast-like morphology but remain positive for HMB45 (h) and NSE (i). Scale bars = 50 μm
